As if there was nothing left to worry about, the bed bugs, the pests of the old bedtime poem, are back. They cause more discomfort than happiness and have been spotted sucking blood from people in hotels, student centers, and clinics. Learn useful information about bed bugs, including what they are, where they hide, and how to find them before they attack.

Know your enemy
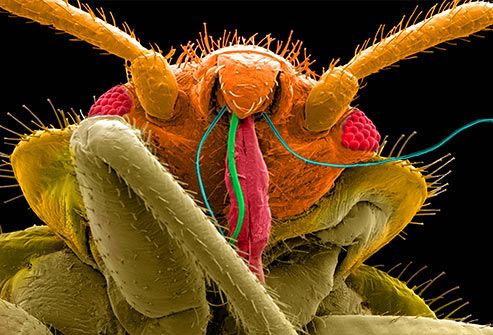
Bed bugs are small, flattened, wingless insects with six legs that feed on the blood of animals and humans, much like mosquitoes. They vary in color from an almost snowy white to a coffee brown, but change to a rusty red when fed. Bed bugs never exceed 0.5 centimeters in length and can be seen with the naked eye by a keen observer. They are so named because they prefer to hide in bedding and mattresses.

Is there a risk of infestation?
Bed bugs are most commonly found in hotels, hostels, shelters, and apartment complexes where many people come and go. Because bed bugs hide in small crevices, they are more likely to enter homes with luggage, pets, furniture, clothing, boxes, and other objects. Bed bugs are found throughout the world, but are more common in developing countries. Once rare in North America, their numbers may now be increasing to some degree due to increased international travel.

Diet
These nocturnal animals may hide during the day in beds, floors, furniture, wood, cardboard waste, etc. We humans are their dinner at night, and their chewing power is at its maximum just before sunrise. They have the opportunity to move in as little as three minutes, after which they will bloody up, leave their owners, and burrow down to digest their food. Food. Bed bugs can exist for up to 10 months, and it is quite possible for them to go months without food.
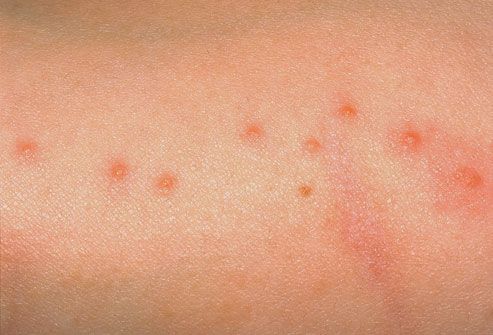
Signs and Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites.
Surprisingly, these little blood-sucking animals eat you without waking you up. You will not notice any noticeable bites because anesthetic drugs are injected into the body along with anticoagulants to keep the blood flowing during the blood sucking process. The first symptom of bed bugs is reddish, itchy bites on the skin (usually the arms and shoulders). Bed bugs tend to leave a single line of bites.
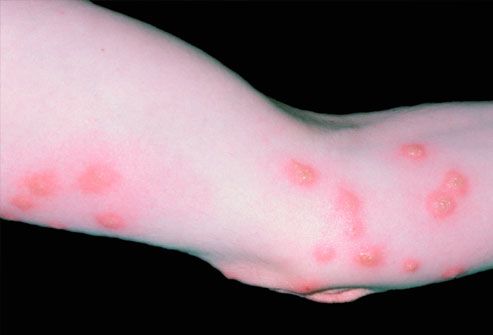
Treatment of bed bug bites
Bed bug bites usually do not heal quickly. If a secondary infection occurs (usually from scratching), apply a topical antiseptic lotion or antibiotic cream or ointment. For early, bothersome itching, corticosteroid creams and oral antihistamines are used. For more serious cases such as this, a physician should probably be consulted.

Do bed bugs transmit disease?
Bed bugs are a problem rather than a health threat. In a recent study, researchers reviewed 53 recent studies on bed bugs and their impact on health and well-being. The results indicated that bed bugs are responsible for spreading as many as 40 different human diseases, but there is insufficient evidence to support that bed bugs are vectors of human diseases.

Is it a bed bug or a scam artist?
Do not assume that you have been bitten by bed bugs. Bites are not easily recognized, even by medical professionals. Visual inspection will eliminate mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, and biting mosquitoes. Collect and identify bed bugs and show how they bite. Search for. the bugs themselves and their blood stains, especially along mattress seams. In addition, look for black spots of insect excrement where bed bugs have every opportunity to burrow into hiding places on furniture, walls, and floors.

Bed bug bites.
Professional exterminators must take immediate action. Notify the landlord, supervisor, clinic manager, or hotel owner or call the exterminator immediately. Exterminators are, bed bugs (Eradicate as needed (can occur in multiple locations). A large amount of laundry will be required.
View source
Photo of Danna:.
(1) Getty Images (2) Nigel Cattlin / Visuals Unlimited (3) Brand (7) Darlene A. Murawski / National Geographic (8) Courtesy of Orkin, Inc. (9) Thinkstock
New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Ohio State Laboratory Extended Fact Sheet. Kentucky Agricultural Research Institute. Nebraska-Lincoln Laboratory Expansion Facility, Lancaster County. Washington Post.






