Many readers are interested in the appropriate subject: taste sensors. Our manufacturer is pleased to report that we have already conducted a study of current research on the subject that will fascinate you. We can give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys. Keep repeating to find out more.
For example, taste Your back button tongue You are particularly sensitive to bitterness. tastes This is probably an evolutionary personality trait. Toxic drugs often contain a connection taste Register Budgies as bitter and annoying. Identify something – something annoying (and potentially dangerous) in the way you take it has the opportunity to save your life.
Anatomy of Taste
The taste bud is a small organ located at the front of the tongue. the tongue . The adult human tongue It contains 2, 000 to 8, 000 taste buttons, each of which is composed of 50 to 50 150 taste receptor cells. Taste receptor cells are important for signaling of taste to the brain.
They believed that it the tongue divided as a map of sections. Salt, flavor became serious to taste bitter, sour. Scientists had learned not so long ago taste to repair each of these parts. the tongue Every kind of of taste quality.
The most common taste Disorders include phantoms taste Observation, position taste Even if there is nothing in the mouth, it is present. Discoverability, the condition it stains taste Retention in the mouth. And burning mouth syndrome.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1097879026-1fb29e2e076840f9b0e3ae029fbb8c8e.jpg)
Anatomy
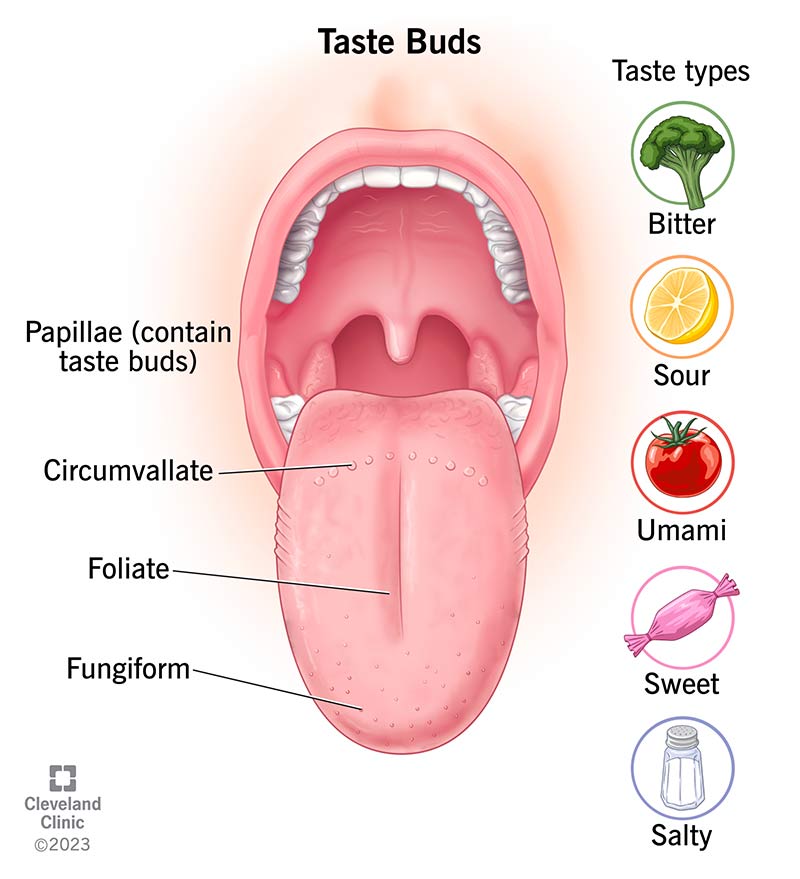
The taste sensor is present in the mouth in a small ridge to you tongue called the papillae. They can also be found in other parts of the mouth, such as the palate and pharynx. There are four similar papillae
- Filiform: very common and covers a strict surface. the tongue And includes taste buds
- Fungal: close to the anterior portion the tongue
- Surround: close to the posterior part the tongue
- Foliate: located on the lateral side the tongue
Taste sensors are developed in the uterus and researchers believe they work at 10 to 13 months of gestation. Fruit can to taste Food from the mother’s food pass through the amniotic fluid. Taste from the mother’s food is still detectable in breast milk.
Function
The taste Receptor cells up taste Budchia is responsible for creating, sending observations to of taste to the brain. These cells regenerate quickly and have an average lifespan of only 8 to 12 days.
The human brain is ready to identify five essential tastes :
- Bitter
- sweet
- salty
- Pickles
- Wooooo.
Most people are the difference between these categories of tastes , not everyone tastes similar. It passes through how taste Popeyes detect certain molecules that range from person to person.
Super Tasters have more papillomas per se. tongues who have the ability to overpower scents. As a result, supertasters love meat foods. Sub-tasters, on the other hand, have fewer papillae. For example, they are less sensitive to strong flavors and keep more embodied aromas and spicy foods.
Myths about taste buds
It is a myth that taste Tasty, salty, bitter, and sour buttons are found in their different parts the tongue Fielding current research shows that once a region is not taste difference. the tongue In fact, scientists now know that all taste Buttons can reveal what is tasty, salty, sour, and bitter tastes regardless of its location.
Relative Disorders
Taste disorder strikes more than 200, 000 people each year. Researchers believe that 15% of adults are likely to have a problem taste or taste. Almost all of them do not find healing.
Phantom taste A perception called abnormality is more common. taste This is a disorder characterized by prolonged taste Often sad or sour, even if there is nothing in the mouth.
If a person has a diminished ability, there is a low tone to taste of things. Absolute accessibility of power. to taste everything is called ageusia. The real taste loss is not common. It is not uncommon for inability to taste associated with loss of taste due to obstruction.
Burning mouth syndrome is a painful condition in which someone experiences a burning sensation in the mouth. Sometimes it can last for months. It is more common in the elderly.
Taste disorder is usually considered a result of illness or injury. People rarely suffer from it. Ear infections, upper respiratory tract disorders, cancer radiation, certain medications, ear, nose and throat manipulation and dental problems can all contribute to personal problems. to taste disorders.
Loss of taste Taste is considered one of the more reliable properties of Covid-19. Researchers believe that infection of some cells that help clog neurons (loss of odor) is the cause of anorectal disturbances.
It is not uncommon for people to burn tongues about passionate foods and drinks. Injury the tongue also occur frequently. You can get yours tongue result of another injury or during dinner. You can still get traumatized by your tongue by dental braces or mouth jewelry.
A swollen tongue Known as glossitis. If you have tongue inflamed, it still has the option of your taste Buttons and rare taste in your mouth. Glossitis can occur as a result of an allergic reaction, trauma, infection, or a side effect of medication.
Pay attention to the swelling and seek medical assistance if it continues to worsen, as all swellings in the mouth can indicate an allergic reaction. to tongue Therefore, pay attention to the swelling and consult a physician thus.
Tests.
Taste disorders are diagnosed by an ENT physician. Symptoms of taste Taste disorders have every opportunity to mask this baggage. of taste or smell, or tastes At some point, what was once pleasant becomes unpleasant.
The physician will determine your perception of smells along with a physical examination and a description of your condition. and taste Observation. This may include measuring the lowest intensity of chemicals that can be distinguished by comparison. taste aromas of various chemicals, and a scratch-and-sniff study.
Treatment for taste Every opportunity to adjust any medications being taken if there is a physical health problem. of taste Taste and underlying health conditions can be identified and corrected, oral blockages that may be causing problems can be identified and removed, and smoking can be stopped.
Taste disorders can affect your ability to eat enough food because if food doesn’t taste good, you are less likely to eat it. taste Yes, you may be less inclined to eat as often or as balanced a diet as you normally do. If you notice a loss or change in self-esteem, it is important to consult your health care provider. of taste or smell.
Treatment of burning mouth syndrome includes pain relief. Some antidepressants and benzodiazepines have also been shown to be effective.
Residential healing is usually done for minor burns the tongue enough. Drinking cold water can help relieve pain and prevent continued tissue destruction from the burn. If you have chemical burns, do not swallow the water, but pour the water over your body. tongue Do not swallow or immediately contact a poison control center or 911.
If a swollen tongue If it is believed to be an allergy, especially if it is a sign of anaphylaxis, the treatment will be to reduce swelling. Your health care provider will continue to work with you to identify the cause of your triggers, including reducing the frequency of triggers.
Home remedies for mild swelling include salt water baths, sucking on ice to reduce swelling, and ignoring foods that are likely to cause tension. tongue such as sour or salty foods.
Most tongue Injuries are minor and heal spontaneously. More severe cases may require stitches and medication. Home healing includes using flexible items, sucking on ice or popsicles, and rinsing with warm salt water.
Very Wellness uses only quality information from peer-reviewed studies to set a precedent in our notes. Read about our editorial process to learn more about how we set a precedent and keep our content clear and credible.
- National HIE for Hearing Impairments and Other Communication Disorders. taste disorders.
- Barlow L., Klein O. of taste Fieldin: current topics in the biology of becoming. 2015; 111: 401-419. doi: 10. 1016/bs. ctdb. 2014. 11. 012.
- Hutchins M. Peroral – An integrated lesson on chemosensory system function. Texas Research Institute.
- Brann D, Tsukahara T, Weinreb C et al. Non-neural expression of the SARS-COV-2 input gene in the olfactory system implicates mechanisms underlying Covid-19-related aneurysms. sci Adv. 2020; 6(31):EABC5801. doi: 10. 1126/sciadv. abc5801.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. The Smell. and taste disorders.
As an unreliable writer, Kathy Vallely has the ability to write about the characteristics of government publications and essays on the topics of health, defense, and education. Most of her work focuses on juveniles, education, health care, and public faith education.
Taste buds
Taste buds are cells in your stomach. tongue You can see tastes how tasty, salty, sour, sad, and acidic immeasurable amounts. Taste sensors regenerate about every 10 days. This means that actually injured taste The button is usually repaired autonomously.
Summary
What are taste buds?
The taste sensor is a small sensory organ that allows you to experience taste Verdades come from within the small ridges that cover the skin. tongue They are called papillae. The taste sensor gives you an aristocracy of what you eat, drink and drink it autonomously. it tastes “Is it good or bad?” This information helps you move comfortably and keep You. taste Poplab alerts you when something is dangerous, such as rotten milk or spoiled beef.
What tastes can taste buds detect?
The taste sensor detects five basic creations tastes , including:
- Sweet: Flavorful foods generally contain some form of sugar (sucrose, glucose, fructose, lactose). This includes foods such as honey, fruit, and ice.
- Salt: Salty foods contain kitchen salt (sodium chloride) or mineral salts such as magnesium and potassium. Think of these foods as pretzels, chips, film centers, etc.
- Bitter: bitter coals have the ability to retain these ingredients, such as caffeine and connections from the plant, among other plants. Bitterness is complex. taste In that regard, you are. taste Batons make sure it is “good” or “bad”. For example, some people like bitter foods, such as coffee or pure chocolate, while others do not.
- Sour: Acid foods such as citrus fruits and vinegar often contain some form of acid (acetic, citric or lactic acid).
- UMAMI: Razumami is a special, rich, or meaty flavor. You will find numerous products taste Umami has a substance called glutamic acid, which is why it was modified in the registration. Razumami foods include tomatoes, asparagus, fish, mushrooms and soybeans.
Your taste Buttons feel it. tastes All kinds of configurations make eating and drinking skills even more difficult. For example, taste Poprav has the ability to register movements so that a delicious but salty imami leads Or drink may taste Leiden Sad but not delicious.
Function
What do taste buds do?
The taste sensor works with the sense of smell in the nose to create a taste experience. When you chew food, your teeth and saliva work together to break it down. This breakdown causes chemicals from the food to release it to you! taste These chemical signals flow through your nasal cavity to sensors in your nose. Putting these signals from your nose and mouth together ensures that your preferences are experienced. For example, the way you hold your beak does not prevent you from tasting something, but it may alter the taste or reduce tension.
Other cells in the mouth and throat contain sensors that register how passionate or icy the ambrosis or drink is. Hot” includes temperature and herbs. The “cold” includes temperature and specific taste sensations such as mint or eucalyptus.
Numerous sense cells work together to shape your eating and drinking habits.
Anatomy
How many taste A person’s button?
The average adult has between 2, 000 and 10, 000 taste buds. We lose taste It means more for boys, since they recover as they get older taste Then there are adults for buttons. Dimensions and numbers of taste positions vary from person to person.
These differences mean that but they all detect the same 5 tastes Observation and skill in this tastes vary.
How big is a taste bud?
Taste sensors have different volumes. On average, they are 30 mm in diameter and 1/16 mm long.
Where are taste buds located?
The taste sensor usually covers the taste bud. tongue The least degree you still have taste Roof of the mouth and throat box. The taste buds on your tongue From the inside it is called a papilloma. There are three similar papillomas that include taste buds:
- Mushrooms: have the sides and the tip of your tongue Paalze contains an estimated 1600 taste buds.
- Bypass: is located behind you tongue The field is about 250 taste buds.
- Foliate: is on your back tongue bilaterally. There are 20 of these papillomas, containing hundreds taste buds each.
It is a popular misconception that your own tongue contains taste Areas that are normally limited or specific areas one taste . Instead, taste Tasty, salty, bitter, sour, button spread throughout your body. tongue Your field tongue Specific is a little more sensitive to tastes .
For example, taste Your back button tongue You are particularly sensitive to bitterness. tastes This is probably an evolutionary personality trait. Toxic drugs often contain a connection taste Register Budgies as bitter and annoying. Identify something – something annoying (and potentially dangerous) in the way you take it has the opportunity to save your life.
What do taste buds look like?
Imagine for yourself a set of cells arranged like a peeled orange or a rainbow bud. On top of the rosebud is a small hole through which… a taste In the pores where the food and drink inside come in contact with the cells, taste .
What kind of structure? a taste bud?
A taste A button is a set of cells grouped inside tongue called papillae. A taste bud includes:
- Taste sensor cells: optional taste The buds contain 50 to 150 taste receptor cells. These cells contain sensors that extend upward. the taste Poretie Extensions. are taste These hairs are called microvilli. Microvilli come into contact with chemicals in the food or drink you consume. Taste sensor cells are connected to nerves… taste They send signals to your brain. Your brain perceives the chemicals that come into contact with the sensors as tasty, salty, etc.
- Basal cells: these cells are considered stem cells and eventually become taste Receptor Cells. Your body replaces taste receptor cells about every 10 days.
- Supportive (Santicentric) Cells: These cells are spread throughout the body. taste buds alongside taste Receptor Cells. But they are inside you. taste no chance of getting a button. taste .
How often do taste buds change?
Basal cells develop as follows new taste receptor cells every week or two (average 10 days). Our taste As you age, the number of repairs decreases, which means that your perception of taste changes at different stages of life. The foods you prefer as an adult have every opportunity to distinguish themselves from the foods you preferred as a child. In the same way, taste As you grow up, your perceptions change.
Symptoms and Disorders
Which other symptoms or disorders affect your perception? taste buds?
A group of criteria called taste Disorders replace your sense of of taste . They include:
- Ageusia: absolute loss of taste .
- Taste disorder: distorted sensations of taste .
- Hypersensitivity: bloating of taste .
- Tastelessness: loss of sensation of taste .
- Phantom taste Disorder: something unpleasant taste These symptoms remain even when there is nothing in the mouth.
Apart from that, each of the actual has the ability to affect you taste buds, causing food to taste differently:
- Infections of the mouth and throat, such as gingivitis.
- Inflammation of the mouth.
- Vitamin B12 or zinc deficiency.
- Metabolic disorders such as diabetes or hypothyroidism.
- Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and confusional sclerosis.
- Nerve damage.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (chronic acid reflux).
- Smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Heavy alcohol use.
- Certain medications, including chemotherapy.
- Dry mouth.
- A burned tongue .
- A swollen taste bud.
Concerns
How can I keep my taste buds healthy?
The good news is that your own taste cabin will be updated and regenerated regularly. Injured taste booths are usually repaired naturally. Rare infections and secondary damage from smoking can harm your taste impede healing and affect your sense of well-being. of taste .
To prevent injuring a taste bud:
- Do not use tobacco products.
- Limit alcohol intake.
- Take care of your teeth and gums. and tongue (oral hygiene).
- Allow food to cool before eating.
- Do not place frozen food directly on your body tongue .
Note from Cleveland Clinic.
The taste sensor is a small sense that requires much work. You experience the sense of taste as reliably as you do the sensors in your nose. If you are suffering from a taste buds, it will probably heal in a week or two and you will be able to enjoy eating again. In the meantime, prevent injury by replacing food and drinks before eating or drinking. Be aware that the use of tobacco products can be detrimental to your body in the long term. taste buds.