Many readers are interested in the right subject, Streptococcus pneumoniae. Our makers are pleased that you have already conducted a study of current research on the subject you are interested in. We can give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating for more information.
Streptococcus pneumoniae was first identified and isolated by Louis Pasteur in 1881. The word “strep” means “twisted” and “coccoid” originally meant “berry.” pneumonia ‘ This part was named after the precedent that bacteria tend to settle non-gravitatively and often have a good chance of it pneumonia Veld that the bacterium is usually derived from steam is also called pneumonia diplococcus.
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae?
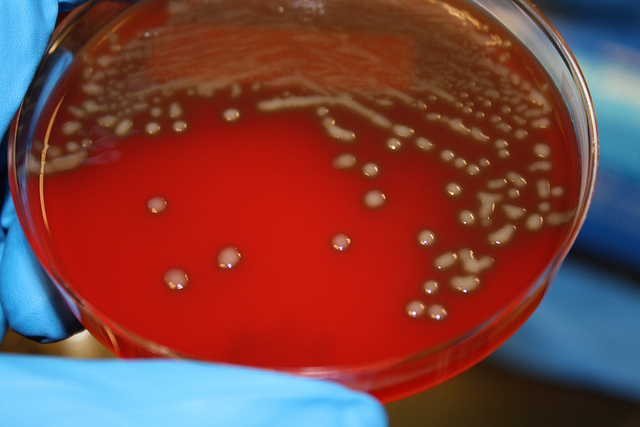
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a strain of microorganism that usually has a slightly pointed cocci shape. They are often found in pairs, but it is still possible to find shorter chains and individual cells. These bacteria refer to the way they break red blood cells. Individual Streptococcus pneumoniae streptococci are generally defined as 0, 5 to 1, 25 micrometers in diameter. Streptococcus pneumoniae are non-motile and do not form or call for female signs, but usually have pilis that are sometimes used to bind themselves to host cells for the best rise. These bacteria are usually observed naturally in the nose and larynx, as well as in the upper respiratory tract. They thrive at temperatures within 30 degrees Celsius.
What is the cellular structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
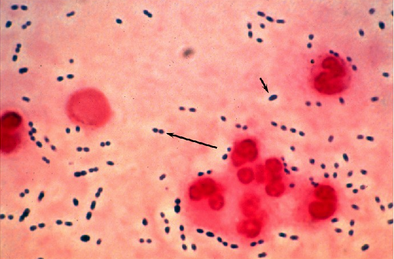
In general, Streptococcus pneumoniae is completely covered with a polysaccharide capsule, making this an efficient microorganism. His cell wall is made of six wide layers of peptidoglycan and lipoteic acid, attached to the membrane by lipid fragments. This lipid contains phosphorylcholine. In addition, Streptococcus contains pneumococci from up to 500 different surface proteins, including CBP or choline-binding proteins. Twelve proteins from this genus are associated with the choline portion of the cell wall, which helps the microbe attach to other active components on the microbial plane. However, as with other filaments, there is no catalase. of streptococci Glucose must be fermented to produce lactic acid. streptococci Streptococcus pneumoniae insulin in a similar manner.
Most of the nitrogen and carbon that the bacteria get is through extracellular enzyme systems. They enable the metabolism of hexosamines and polysaccharides, which work to damage the owner’s fabric and actually allow colonization. In fact, they make Streptococcus pneumoniae very effective if they find the owner.
What diseases can cause pneumonia?
As mentioned earlier, one of the more popular diseases caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae is the situation where a non-serious disease is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. is pneumonia This is a situation in which the lungs and the vesicles of the non-serious patient become inflamed as a result of the infection. Pneumonia caused by these microorganisms is a four-step process. In the first step, the lung follicles of the non-weight bearing owner are filled with serous humidity and, according to scientists, are stimulated by the cell walls of Streptococcus pneumoniae. This organism in the water actually spreads into the non-energetic leading to stage 2, where the mesangial cells penetrate the alveoli. More red blood cells are still attracted to the space. During Stage 3. of pneumonia If Streptococcus pneumoniae is not found and does not die, the microorganism may survive in the bloodstream and then end up in the bloodstream. If Streptococcus pneumoniae is undetected and does not kill, it may survive non-vigorously and the microorganism may more easily penetrate the brain, infect the meninges, and cause meningitis.
Besides meningitis and pneumonia There are many other diseases associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae, including sinusitis, and otitis media, in which the middle ear is infected. Streptococcus pneumoniae can cause pneumonia, inflammation of the peritoneum, and arthritis.
How to Diagnose Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection
To detect and treat Streptococcus pneumoniae, a gram color should be performed on the patient’s sput. The presence of neutrophils in the sample, as well as a positive bilinear flow greater than 10 grams, will identify the bacteria. If the test results do not provide a definitive answer, or if further testing is needed, the bacteria can be further counted and analyzed via the Blood Agara strip method. When this test is performed, the Streptococcus pneumoniae must show alpha-hemolysis. This will result in areas where there is a greenish color to the blood around the microbial colonies placed on agar. However, this test is not always considered definitive because other members of Streptococcus can show a similar reaction and cause alpha-hemolysis. To make this test convincing, the striped organism must still show affection for occultin or GAL. This can justify being more impressive that the bacterium is Streptococcus pneumoniae.
How to Treat Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection
Depending on how serious the infection is and how long someone has been suffering from it, there are different treatment options for people suffering from Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.
If the infection is very serious or has persisted for a long time, penicillin is often given, while for less serious cases penicillin V is used more often. Unfortunately, more and more tribes of Streptococcus pneumoniae are resistant to penicillin, and this is usually because of the way they are resistant to various types of penicillin; certain tribes of Streptococcus have developed pneumoniae stability to this healing method, so it is possible that other tribes will develop similar Because it is very likely that stability will develop quickly, researchers must find another method of cure. However, it is very tempting for Streptococcus pneumoniae to become penicillin-resistant, since it naturally increases fairly rapidly and has the ability to create huge cell densities by its own infectious standards.
Fortunately, researchers are now working to develop erythromycin as a drug for pneumococcal infections, as it has been shown to be effective against penicillin-resistant microtubers.
Based on the above information, prevention is often more important than cure in the case of Streptococcus pneumoniae, and fortunately, vaccines are still available to help prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae from penetrating and causing infection. The vaccine contains a 23-valent membrane polysaccharide that has the ability to defend itself against the more common disease strains. However, for example, because there are numerous different types (at least 90 different tribes) and are constantly being developed, vaccines are not effective against all tribes and can suffer from Streptococcus. Pneumonia infection even after such a vaccine. & lt; pran & gt; Based on the above information, prevention is often more important than treatment in the case of Streptococcus pneumoniae, and fortunately, vaccines are still available to help prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae from penetrating and causing infection The vaccine is still available. This vaccine contains a 23-step capsul-like polysaccharide that has the ability to defend itself against the more popular facultative family. However, the vaccine is not effective against all tribes and can suffer from Streptococcus, for example, because there are numerous different types (at least 90 different tribes) and are constantly being developed. pneumonia infection even after such a vaccine. Preventive measures are based on the above information






