Many readers are interested in the right subject: the anatomy of the shoulder joint. We are pleased to report that our makers have already done research on current studies on your fascinating subject. We can provide you with a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys. Find out more.
The shoulder joint One of the most important and smooth impressions joints between the axial and upper appendicular portion of the human body.2 Large joints —the glenohumeral joint and scapulitis. joint in the shoulder Glenohumeral helps with the smooth movement of the tool. joint Is responsible for most shoulder from movement, but to gain strength and reasonable movement thereafter, scapulitis joint functioning quite well. Usually, the shoulder joint refers to Glenohumerale. joint Veldin this post we will determine and explain in detail anatomy of the shoulder joint .
Anatomy of the Shoulder
Bones: 3 bones. the shoulder – Shoulder lobe, clavicle, top arm bone. 3 bones are joined Together by ligaments, tendons, and muscles covered by a by joint platform function and hairstyles that provide a platform for movement.
Joints: The major joint of the shoulder is glenohumeral joint This is formed by the ball-shaped head of the humerus and the glenoid fossa-shaped cavity of the lobule.
Soft tissues: Bones and joints It is covered almost entirely with folded tissue. The delta muscle may be the top layer of flexible tissue under the skin. The next layer below the delta muscle is the bursa subdertoidus, which forms a weightless ball-like pouch filled with fluid.
Besides, the shoulder It also helps build the scapula at the chest wall.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
Basic movements around the the shoulder joint Turning the arm in a radial motion or swinging the arm from the body can actually lead to grenohumerare joint —also known as shoulder joint We will look at the following the shoulder joint anatomy .
1. bones
The humerus (upper arm) and scapula (shoulder blade) are the two most important bones upon which the shoulder and scapula are built. the shoulder joint anatomy The ball head of the humerus is described by the large volume of the scapula, which is described by the large bowl of the scapular head. Because of this difference in volume, the bones cannot fit together seamlessly without the support of other surrounding flexible tissues the joint , which provide the joint Strength Factor.
2. cartilage
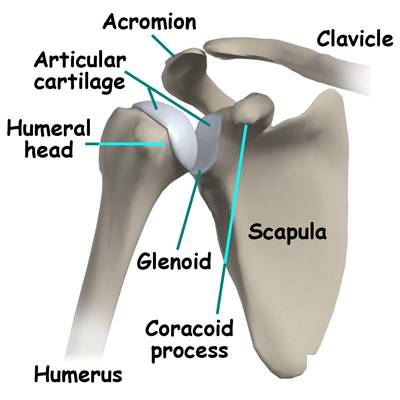
The most important articular cartilage, the lip, lies between the humeral head and the chiossa glenoid. the shoulder joint The lip is a ring-shaped cartilage with a central, graceful, thick rim. The particular structure of the lips ensures that the large humeral head fits easily into the small glenoid bowl. Thus, the lips are not only important for joint not only for stabilization, but also for smooth and free movement around them shoulder joint minimize friction.
3. muscles
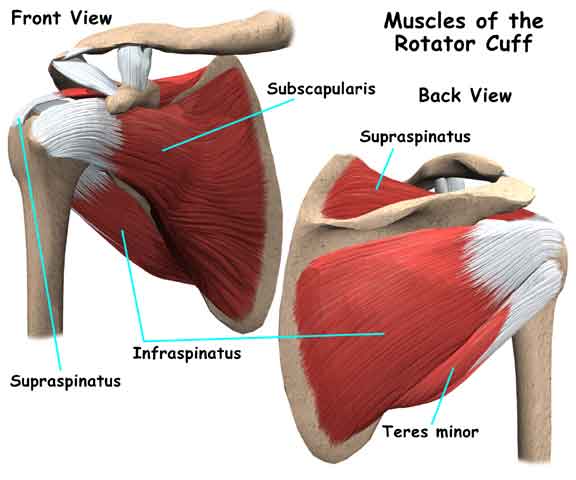
The most important muscle group the shoulder joint The rotator cuff is called the cuff and consists of the suspaspine, scapular, plantar, and small round muscles. The rotator cuff connects the false bones to the scapula up to the scapula, which connects the head of the upper arm to the small joint bowl of the scapula.
The rotator cuff not only stabilizes the scapula but also helps prevent injury. the shoulder joint anatomy However, it can also be damaged by the shoulder joint Disruption. Arm. the shoulder joint The rotator cuff can also aid in the rotational movement of the rotator cuff, especially the arms. The master adductor muscle helps move the arm away from the body. Therefore, this muscle is more sensitive to injury during bending and reflating movements.
4. ligaments
Ligaments around the shoulder joint further stabilize the joint anatomy And movement around it. there are enormous ligaments in the three humerus posterior and one beak. Later. joins Collacoids escape from the scapula to the humerus, as the name footprint continues.
5. joint capsule and brusa.
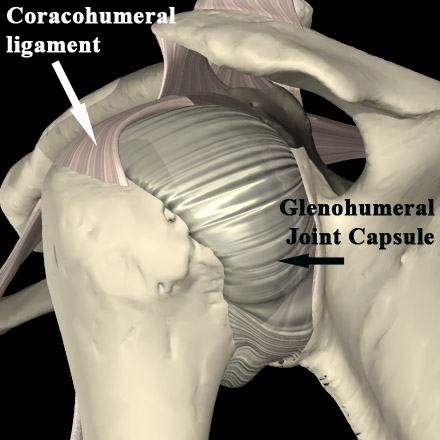
The joint The hairdo is a fibrous sheath of structure the joint The structure extends from the neck of the humerus to the end of the joint cavity. The joint The hairdo is attached smoothly to the greatest movement around the shoulder joint . Friction is minimized by the synovial water characterized by the synovial sheath attached to the inner surface. the joint Haircut. To further reduce friction, the synovial fluid and purse relax the plane between the tendons of the rotatory and other muscles. joint Structure. Very important brutes around the the shoulder joint Subaccumulation and subcutaneous bursa. The cervical articulations support the surrounding muscles, such as the deltoid and supraspinatus, while the subcutaneous articulations reduce damage to the surrounding muscles. the shoulder joint during the joint mobility.
6. nerve and blood supply.
The blood supply of the shoulder joint The brachialis is derived from the anterior and posterior portions of the rflex bone and its branches also form anastomoses around it. the joint It also ensures the supply function.
Innervation occurs from roots C5 and C6 of the brachialis plexus, which includes the a fossa nerve, the superior cranial nerve, and the lateral thoracic nerve. Thus, paralysis of the Erb, damage to roots C5 and C6 of the cerebral plexus, Bexus brachialis. the shoulder joint functions.
To better understand the shoulder joint anatomy For more information on visual information, please watch the video.
Common shoulder problems
With the shoulder joint anatomy It is possible to detect some known problems better than others. on shoulder The following are well known The following are well known
- Frozen shoulder: In this condition, movement is very limited. the shoulder joint It is severely limited by the inflammatory process in the shoulder. the joint anatomy You have pain and stiffness. And you can experience pain and stiffness.
- Osteoarthritis: This is a result of aging comparable to simple joint wear. the joint structures, but the shoulder joint Less often involved in osteoarthritis than the knee joint .
- Rheumatoid arthritis: this is an autoimmune disorder in which the body is joints attached by the body’s personal defense fighters. any joint The body, including the the shoulder joint It also causes pain and inflammation the joint .
- Cracks in the rotatormanchet: due to overload, aggressive use, or trauma in the area. the shoulder This area has the opportunity to lead to a crack in the rotator cuff, which actually leads to muscle soreness and inflammation.
- Shoulder complaints: this condition refers to the compression of the muscles of the torsion checker against the process of the acromion scapula when lifting the arm. All injuries and inflammation cause pain.
- Shoulder location: the spur of the bone (usually the humerus) from the the joint edge of the – as a result of enlargement of the major coccyx, the joint disruption from his original space. In this condition, there is moderate to severe pain in the enlargement of the arm the joint .
- Shoulder tendon inflammation: this is inflammation of the shoulder tendons. the joint cavity of shoulder .
- Shoulder Bursa: This is an inflammation of the bursa between the muscle tendons and other structures. the shoulder Other structures do. The most important signs are pain and excessive pressure, more noticeable during movement.
- Minor tears: cracks usually occur due to accidental injury the shoulder or its excessive introduction. These fissures in the host heal themselves without surgical treatment.






