Many of our readers are interested in our upcoming content, Flattering and Negative Analysis of Consumption: How to Tell the Difference. Our authors are happy to report that we have already surveyed contemporary research on your topic of interest. We will answer your questions in detail based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers and sample surveys. Please repeat for further study.
Tuberculosis, or elemental ingestion, is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, some strains of mycobacteria. A tuberculin test is performed to determine if the patient has been infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. positive vs negative Tuberculosis test results. In this test, a small amount of tuberculosis-derived protein (PPD) is placed under the top layer of skin on the forearm. If the patient is exposed to tuberculosis, a reddish bump appears at the injection site two days later. While this test is effective, it cannot determine the duration of TB infection or whether the infection is active.
What is a flattering negative TB test result? And what does it mean?
Negative results
When you get a negative A post-test reaction means that you have never been infected with the bacteria that causes ingestion in your life. If the test comes back out negative Little or no swelling will be felt; measurements will be different for HIV and other risk groups.
PPD skin tests are not considered reliable. Some people may have the bacteria but feel little or no reaction after the test. Drugs or diseases that weaken the immune system can cause false negative results.
Positive Results
After performing a consumption test, there is a greater likelihood that the result will be positive. positive . This means that the patient is infected with the bacteria causing the ingestion. However, the disease may not have progressed and may require treatment to prevent recurrence. Additional tests are needed to prove whether the tumor is active.
The tumor is considered to be at least 5 mm in size at the site of examination. positive in:
- HIV Patients
- Organ transplant beneficiaries
- Persons with a compromised immune system or using steroids.
- Persons who have had intensive contact with tuberculosis patients.
- Persons with fibrous or nodular geometry on chest x-ray.
Tumors are considered to be larger than 10 mm within the examination space. positive in:
- People who have negative Results of studies in the past 2 years
- Persons with renal failure, diabetes mellitus, and other conditions that increase the risk of contracting TB.
- Health care workers
- People who inject drugs
- People migrating from countries with the highest rates of TB infection
- Children under 4 years of age
- Minors in close contact with adult risk groups
- People in large settings, such as students, prisoners, homeless populations, etc.
Edema greater than 15 millimeters in the test room will be considered positive in
- People without popular risk points for TB
If the skin test rash changes out positive The physician may order imaging tests, such as chest x-rays or CT scans, to obtain more information. If these tests show that you have TB, arrange for future testing of your sput to look for TB bacteria.
Who should have a TB test?
TB is one of the most contagious diseases and is considered one of the largest causes of death. According to the World Health Organization, it is the second and AIDS. If you work in health care, you should undergo routine TB screening by taking the PPD skin test. You must still the positive vs negative TB test if:
- You are in close contact with someone who has TB.
- Your immune system is vulnerable to the disease or the drugs.
How can I prepare for the TB test?
You must tell your doctor before you take the PPD test. whether you have had adverse reactions to tuberculin tests in the past:
- Have you had tuberculin test side effects in the past
- Signs of TB such as coughing, sweating, inexplicable weight loss, etc.
- Tuberculosis has been established in the past
- You have risk points for TB (e.g., travel to a country where TB is common, near a TB patient)
- There has been TB vaccination
- Use drugs that affect your immunity (e.g. corticosteroids)
- HIV
- You have a skin rash that can make reading test results more difficult
- You are concerned about the test, the risks, or how the test is performed
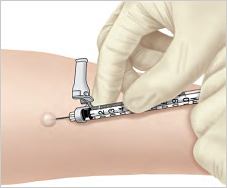
How the Tuberculoet test is performed
To do the positive vs negative With the Tuberculoet test, the physician first takes a smear from the skin on the inside of your forearm. Next, the physician will inject PPD under the top layer of your skin. You will feel a light sip. There will be a small walk or bump that will disappear over a specific number of hours.
It is your responsibility to provide proper care to prevent confusing test results.
- Do not cover the test web site with tape or bandages.
- Do not scratch or rub the test site
- Add cool material in case of itching
- Wash hands and dry carefully
Should return to the physician after 2 or 3 days. Find out if he/she has reacted to the injection where you received the PPD sting. Usually, there is little chance of swelling or redness swelling. Especially if you have already had a PPD test and are performing it again.








