Many readers are interested in the right subject: adult otitis media medium. Our manufacturer is pleased to report that we have already done modern research studies on your fascinating subject. We will give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating it for more information.
Ear infections have a chance to be disastrous. Middle ear infections, also called as otitis media Everyone, young and old, can meet with one. It is more common in children because of the smallest tube of Eustachius that drains the ear into the larynx lilly. but otitis media in adults It can also occur on almost any different basis. Middle ear infections can be caused by cooling, sinus infections, or allergic drainage. Isolation buildup can cause swelling that cultivates bacteria in the ear and blocks the tubes of Eustachius. This can cause uncomfortable pain.
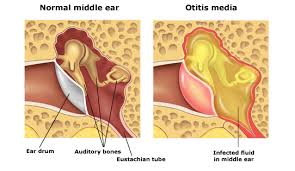
Occasionally, the middle ear may produce fluid months after an ear infection. otitis media with exudate. The moisture stays in place over time, allowing the bacteria that cause the infection to form. The fluid cannot escape completely, causing chronic otitis media . Untreated otitis media It can lead to hearing loss, balance issues, and other problems. This post will certainly help you know more otitis media in adults and what you can do about it.
Causes and Signs of Otitis Media in Adults
Causes
Otitis media Otitis media is usually considered an inner ear infection, which can be caused by bacteria or microorganisms. These viruses grow from the larynx through the Eustachian tube into the inner ear. They usually enter with the throat when there is a large amount of moisture due to cold or allergies. In this case, the moisture rises into the ear and reaches the eardrum.
If there is an infection in the sinuses, throat, or upper airway in the nose, the Eustachian tube may swell and become hidden. Moisture is then left behind from the middle ear, which must be removed. Bacteria love to grow in this because it is warm and wet. The longer the fluid stays in, the greater the chance of infection. It occurs more frequently in adults sinus problems and allergies.
Symptoms
The main symptom of otitis media in adults Ear pain. Other symptoms include
- Sensation of ear set-up
- Trouble
- High temperature
- Headache
- tinnitus in the ears
- Dizziness
- nausea
- vomiting or diarrhea
- Leakage of fluid from the ear canal
How to Treat Adult Media Otitis Media
Viral ear infections heal automatically without the need for antibiotics. The physician may suggest anti-inflammatory medications including anti-stability and anesthetics. Apart from time, there are many things that can be placed during an ear infection.
- Anesthesia. Doctors can recommend freely available anesthetics and ignition inhibitors such as ibuprofen to reduce swelling and annoying pain. If available, they can certainly help lower fever as well.
- Warm Compression. Take a jug and fill it with warm water. You can also place a wet, clean towel in the microwave for about 20-30 seconds. Make sure you know the temperature before you put it in your ear to prevent burns. Another trick is to fill the sock with white rice and tie it on. Burn it in the microwave for 30-45 seconds, check the temperature and then apply it to the skin.
- Continue with your own doctor. If you go to your own doctor for an earache and initially say it is viral, go to the doctor again if the earache persists or gets worse. There is a bacterial infection that can occur after a viral infection and you need medication for that.
- Ask for narcotic ear drops. There are narcotic ear drops that the doctor can prescribe. They are probably not used in the case of a ruptured eardrum, but they are used in the case of non-vigorous or moderate otitis media. of otitis media without rupture.
Acute otitis media.
Acute inner ear infections are more common in boys, but adults can also get it. Healing is as follows
- Painkillers as needed
- Antibiotics
- Oral or nasal steroids if the underlying cause is allergy related.
If the above interventions do not clear the infection, the physician may opt for a “myotomy”. With it, the physician surgically opens the eardrum and removes pressure. Since medications and anti-inflammatory drugs usually help to cure the infection, this procedure is no longer performed frequently.
For ruptured acquired inflammatory media.
Ear infections that cause ruptured eardrums can often be treated with antibiotic ear drops. Your doctor will tell you how to unlock your Eustachian tube to make room for the drop. Faster and with the least negative outcome.
More Home Remedies for Otitis Media in Adults
Always consult your doctor before using home remedies. Proper remedies have been used for centuries to relieve earaches and combat infections.
-
 Olive Oil – Olive oil helps to loosen ear infections and dirt in the ear canal. This can contain bacteria that are more likely to cause infection. Heat the oil slightly and place a few drops in the ear canal. The next day, carefully clean the ear canal with a cotton swab. Be careful not to put the cotton swab in the ear, however.
Olive Oil – Olive oil helps to loosen ear infections and dirt in the ear canal. This can contain bacteria that are more likely to cause infection. Heat the oil slightly and place a few drops in the ear canal. The next day, carefully clean the ear canal with a cotton swab. Be careful not to put the cotton swab in the ear, however. - GarlicGarlic has been used for centuries as a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory agent. Take garlic juice and throw it directly into the affected ear. This helps fight infection when applied three times a day, as opposed to pain. To make garlic juice, cook two to three cloves in water with salt. You can still fold the cloves and place them in the ear after cooking. To keep the infection under control, you will need to burn a few raw garlic cloves daily.
-
 Tea tree oil mixture – Tea tree oil is considered another natural agent that has been used for centuries to cure infections. This is done by mixing 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar with 3 drops of tea tree oil and 2 tablespoons of olive oil to help the ear immediately. Add 1 teaspoon colloidal silver and heat everything together. Place the affected ear and throw some of this into the ear and stay in this position for 5 minutes. Then drain the ear and repeat this twice a day.
Tea tree oil mixture – Tea tree oil is considered another natural agent that has been used for centuries to cure infections. This is done by mixing 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar with 3 drops of tea tree oil and 2 tablespoons of olive oil to help the ear immediately. Add 1 teaspoon colloidal silver and heat everything together. Place the affected ear and throw some of this into the ear and stay in this position for 5 minutes. Then drain the ear and repeat this twice a day.
What are the complications?
Otitis media in adults The following complications can occur
- Infection of the skull bone (mastoiditis).
- Meningitis.
- Facial nerve palsy.
- Temporary abscess.
- Sinus thrombosis.
If an ear infection develops into any of the above complications, it may be necessary to treat untreated ear infections with intravenous antibiotics in the clinic.






