Each of the following products is a combination oral contraceptive containing the progestational compound norgestimate and the estrogenic compound ethinyl estradiol. Norgestimate is designated as (18,19-Dinor-17-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one,17-(acetyloxy)-13-ethyl-, oxime,(17α)-(+)-) and ethinyl estradiol is designated as (19-nor-17α-pregna,1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol).
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 1, 2022.
On This Page
- Boxed Warning
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combination oral contraceptive (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs are contraindicated in women who are over 35 years of age and smoke [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)].
Indications and Usage for Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol
Oral Contraceptive
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14)] .
Acne
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is indicated for the treatment of moderate acne vulgaris in females at least 15 years of age, who have no known contraindications to oral contraceptive therapy and have achieved menarche. Tri-Estarylla™ should be used for the treatment of acne only if the patient desires an oral contraceptive for birth control [see CLINICAL STUDIES ( 14)].
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Dosage and Administration
How to Start Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is dispensed in a blister pack [see HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING ( 16)]. Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP may be started using either a Day 1 start or a Sunday start (see Table 1). For the first cycle of a Sunday Start regimen, an additional method of contraception should be used until after the first 7 consecutive days of administration.
How to Take Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP
Table 1: Instructions for Administration of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP
Starting COCs in women not currently using hormonal contraception (Day 1 Start or Sunday Start)
Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of this product.
- Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP active tablets are white (Day 1 to Day 7), light blue (Day 8 to Day 14) and blue (Day15 to Day 21).
- Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP has green inactive tablets (Day 22 to Day 28).
- Take first active tablet without regard to meals on the first day of menses.
- Take subsequent active tablets once daily at the same time each day for a total of 21 days.
- Take one green inactive tablet daily for 7 days and at the same time of day that active tablets were taken.
- Begin each subsequent blister pack on the same day of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP the week as the first cycle blister pack (i.e., on the day after taking the last inactive tablet)
- Take first active tablet without regard to meals on the first Sunday after the onset of menses. Due to the potential risk of becoming pregnant, use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of the patient’s first cycle pack of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP.
- Take subsequent active tablets once daily at the same time each day for a total of 21 days.
- Take one green inactive tablet daily for the following 7 days and at the same time of day that active tablets were taken.
- Begin each subsequent pack on the same day of the week as the first cycle pack (i.e., on the Sunday after taking the last inactive tablet) and additional non-hormonal contraceptive is not needed.
- Switching to Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP from another oral contraceptive
Start on the same day that a new pack of the previous oral contraceptive would have started.
- Switching from another contraceptive method to Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP
Start Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP:
Starting Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP after Abortion or Miscarriage
- After a first-trimester abortion or miscarriage, Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP may be started immediately. An additional method of contraception is not needed if Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is started immediately.
- If Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is not started within 5 days after termination of the pregnancy, the patient should use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of her first cycle blister pack of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP.
- Do not start until 4 weeks after a second-trimester abortion or miscarriage, due to the increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Start Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP, following the instructions in Table 1 for Day 1 or Sunday start, as desired. If using Sunday start, use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of the patient’s first cycle pack of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP. [See CONTRAINDICATIONS (4), WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1), and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.]
Starting Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP after Childbirth
- Do not start until 4 weeks after delivery, due to the increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Start contraceptive therapy with Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP following the instructions in Table 1 (above) for women not currently using hormonal contraception.
- Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP is not recommended for use in lactating women [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.3)].
- If the woman has not yet had a period postpartum, consider the possibility of ovulation and conception occurring prior to use of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP. [See CONTRAINDICATIONS (4), WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1), USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1 and 8.3), and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling ].
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS
DECIDE WHAT TIME OF DAY YOU WANT TO TAKE YOUR PILL.
The pill pack has 21 active pills (with hormones) to take for 3 weeks. This is followed by 1 week of reminder green pills (without hormones).
-
-
- where on the pack to start taking pills,
- in what order to take the pills (follow the arrows)
- The week numbers as shown in the diagram below
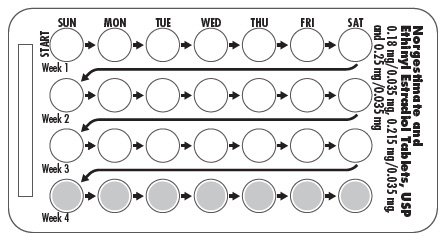
4.BE SURE YOU HAVE READY AT ALL TIMES:
- Another kind of birth control (such as a condom or spermicide) to use as a back-up method in case you miss pills.
- An extra, full pill blister pack.
Missed Tablets
If one active tablet is missed in Weeks 1, 2, or 3
Take the tablet as soon as possible. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished.
If two active tablets are missed in Week 1 or Week 2
Take the two missed tablets as soon as possible and the next two active tablets the next day. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. Additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) should be used as back-up if the patient has sex within 7 days after missing tablets.
If two active tablets are missed in the third week or three or more active tablets are missed in a row in Weeks 1, 2, or 3
Day 1 start: Throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack that same day.
Sunday start: Continue taking one tablet a day until Sunday, then throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack that same day. Additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) should be used as back-up if the patient has sex within 7 days after missing tablets.
Advice in Case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
In case of severe vomiting or diarrhea, absorption may not be complete and additional contraceptive measures should be taken. If vomiting or diarrhea occurs within 3 to 4 hours after taking an active tablet, handle this as a missed tablet [see FDA-Approved Patient Labeling ].
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP Use for Acne
The timing of initiation of dosing with Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP for acne should follow the guidelines for use of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP as an oral contraceptive. Consult the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section (2.1) for instructions
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets, USP Tablets are available in blister cards. Each blister pack contains
28 tablets in the following order:
- 7 white (active) tablets are round, debossed with SZ on one side and T2 on the other side and contains 0.18 mg of norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol.
- 7 light blue (active) tablets are round, debossed with SZ on one side and T3 on the other side and contains 0.215 mg of norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol.
- 7 blue (active) tablets are round, debossed with SZ on one side and T4 on the other side and contains 0.25 mg of norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol.
- 7 green (inert) tablets are round, debossed with SZ on one side and J1 on the other side.
Contraindications
Estarylla™ is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include women who are known to:
- Smoke, if over age 35 [see BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, now or in the past [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have cerebrovascular disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have coronary artery disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Have uncontrolled hypertension [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.4 )]
- Have diabetes mellitus with vascular disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.6 )]
- Have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraine headaches with aura [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.7 )]
- Women over age 35 with any migraine headaches [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.7 )]
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.8 )]
- Pregnancy, because there is no reason to use COCs during pregnancy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.9 ) and USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS ( 8.1 )]
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.11 )]
- Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.3 )]
Warnings and Precautions
Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
- Stop Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if an arterial thrombotic event or venous thromboembolic (VTE) event occurs.
- Stop Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions. Evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.2)].
- If feasible, stop Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of VTE as well as during and following prolonged immobilization.
- Start Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum VTE decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the risk of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
- The use of COCs increases the risk of VTE. However, pregnancy increases the risk of VTE as much or more than the use of COCs. The risk of VTE in women using COCs is 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of use of COCs and when restarting hormonal contraception after a break of 4 weeks or longer. The risk of thromboembolic disease due to COCs gradually disappears after use is discontinued.
- Use of COCs also increases the risk of arterial thromboses such as strokes and myocardial infarctions, especially in women with other risk factors for these events. COCs have been shown to increase both the relative and attributable risks of cerebrovascular events (thrombotic and hemorrhagic strokes). This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age who smoke.
- Use COCs with caution in women with cardiovascular disease risk factors.
Liver Disease
Impaired Liver Function
Do not use Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol in women with liver disease, such as acute viral hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis of liver [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)]. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded. Discontinue Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if jaundice develops.
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol is contraindicated in women with benign and malignant liver tumors [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)] . Hepatic adenomas are associated with COC use. An estimate of the attributable risk is 3.3 cases/100,000 COC users. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (>8 years) COC users. However, the risk of liver cancers in COC users is less than one case per million users.
Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in women using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications, such as COCs. Discontinue Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)] . Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen.
High Blood Pressure
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol is contraindicated in women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)]. For women with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in women taking COCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use. The incidence of hypertension increases with increasing concentrations of progestin.
Gallbladder Disease
Studies suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among COC users. Use of COCs may worsen existing gallbladder disease. A past history of COC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent COC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for COC related cholestasis.
Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Carefully monitor prediabetic and diabetic women who take Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol. COCs may decrease glucose tolerance.
Consider alternative contraception for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia. A small proportion of women will have adverse lipid changes while on COCs.
Women with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may be at an increased risk of pancreatitis when using COCs.
Headache
If a woman taking Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol develops new headaches that are recurrent, persistent, or severe, evaluate the cause and discontinue Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if indicated.
Consider discontinuation of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol in the case of increased frequency or severity of migraine during COC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event).
Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
Unscheduled Bleeding and Spotting
Unscheduled (breakthrough or intracyclic) bleeding and spotting sometimes occur in patients on COCs, especially during the first three months of use. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, check for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy. If pathology and pregnancy are excluded, bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or with a change to a different contraceptive product.
In clinical trials of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol, the frequency and duration of breakthrough bleeding and/or spotting was assessed in 1,647 patients (21,275 evaluable cycles) and 4,826 patients (35,546 evaluable cycles), respectively. A total of 231 (4.8%) women discontinued Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol at least in part, due to bleeding or spotting. Based on data from the clinical trials, 13 to 38% of women using Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol experienced unscheduled bleeding per cycle in the first year. The percent of women who experienced breakthrough/unscheduled bleeding tended to decrease over time.
Amenorrhea and Oligomenorrhea
Women who use Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol may experience amenorrhea. Some women may experience amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea after discontinuation of COCs, especially when such a condition was pre-existent.
If scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (missed one or more active tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and take appropriate diagnostic measures. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, rule out pregnancy.
COC Use Before or During Early Pregnancy
Extensive epidemiological studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in women who have used oral contraceptives prior to pregnancy. Studies also do not suggest a teratogenic effect, particularly in so far as cardiac anomalies and limb reduction defects are concerned, when oral contraceptives are taken inadvertently during early pregnancy. Discontinue Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol use if pregnancy is confirmed.
Administration of COCs to induce withdrawal bleeding should not be used as a test for pregnancy [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1) ].
Depression
Carefully observe women with a history of depression and discontinue Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol if depression recurs to a serious degree.
Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
Estarylla™ is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally
sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast
cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However,
some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users
( Cervical Cancer
A causal relationship between the use of CHCs and the development of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia has
not been clearly established. In observational studies it suggests that COCs are associated with an increase in the risk of cervical
cancer or intraepithelial neoplasia. There is controversy about the extent to which these findings are due to differences in sexual
behavior and other factors.Effect on Binding Globulins
The estrogen component of COCs may raise the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. The dose of replacement thyroid hormone or cortisol therapy may need to be increased.
Monitoring
A woman who is taking COCs should have a yearly visit with her healthcare provider for a blood pressure check and for other indicated healthcare.
Hereditary Angioedema
In women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of angioedema.
Chloasma
Chloasma may occasionally occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma gravidarum. Women with a tendency to chloasma should avoid exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation while taking Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol.
Adverse Reactions
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke [see BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Vascular events [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Liver disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
- Adverse reactions commonly reported by COC users are:
- Irregular uterine bleeding
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol was evaluated in 4,826 healthy women of child-bearing potential who participated in 6 clinical trials and received at least 1 dose of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol for contraception. Two trials were randomized active-controlled trials and 4 were uncontrolled open-label trials. In 3 trials, subjects were followed for up to 24 cycles; in 2 trials, subjects were followed for up to 12 cycles; and in 1 trial, subjects were followed for up to 6 cycles.
Common Adverse Reactions (≥ 2% of subjects): The most common adverse reactions reported by at least 2% of the 4,826 women were the following in order of decreasing incidence: headache/migraine (33.6%), breast issues (including breast pain, enlargement, and discharge) (8%), vaginal infection (7.1%), abdominal/gastrointestinal pain (5.6%), mood disorders (including mood alteration and depression) (3.8%), genital discharge (3.2%), and changes in weight (including weight fluctuation, increased or decreased) (2.5%).
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation: Over the trials, between 9 to 27% of subjects discontinued the trial due to an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) leading to discontinuation were: metrorrhagia (4.3%), nausea/vomiting (2.8%), headache/migraine (2.4%), mood disorders (including depression and mood altered) (1.1%), and weight increased (1.1%).
Serious Adverse Reactions: breast cancer (1 subject), carcinoma of the cervix in situ (1 subject), hypertension (1 subject), and migraine (2 subjects).
Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no
association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 – 1.12 (Figure 2).Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users ( COCs (Figure 2). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies
found an increased relative risk of 1.19 – 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast
cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.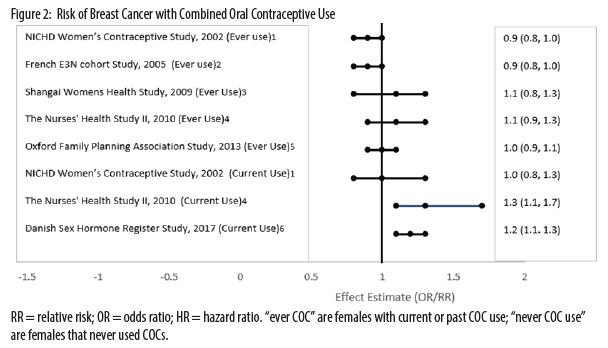
For your reference, below are the studies reviewed by FDA to inform the breast cancer risk:
References:
1. Marchbanks PA, McDonald JA, Wilson HG, et al. Oral contraceptives and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
2002;346(26):2025-2032.
2. Dumeaux V, Fournier A, Lund E, Clavel-Chapelon F. Previous oral contraceptive use and breast cancer risk according to hormone replacement therapy use among postmenopausal women. Cancer Causes Control. 2005;16(5):537-544.
3. Dorjgochoo T, Shu XO, Li HL, et al. Use of oral contraceptives, intrauterine devices and tubal sterilization and cancer risk in a
large prospective study, from 1996 to 2006. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(10):2442- 2449.
4. Hunter DJ, Colditz GA, Hankinson SE, et al. Oral contraceptive use and breast cancer: a prospective study of young women.
Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 2010;19(10):2496-2502.
5. Vessey M, Yeates D. Oral contraceptive use and cancer. Final report from the Oxford-Family Planning Association contraceptive
study. Contraception. 2013; 88(6): 678-683.
6. Morch LS, Skovlund CW, Hannaford PC, Iversen L, Fielding S, Lidegaard O. Contemporary Hormonal Contraception and the Risk of Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(23):2228-2239.Drug Interactions
Consult the labeling of concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with hormonal contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations.
No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol.
Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances decreasing the plasma concentrations of COCs
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), may decrease the plasma concentrations of COCs and potentially diminish the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampicin, topiramate, rifabutin, rufinamide, aprepitant, and products containing St. John’s wort. Interactions between hormonal contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or contraceptive failure. Counsel women to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with COCs, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
Colesevelam : Colesevelam, a bile acid sequestrant, given together with a COC, has been shown to significantly decrease the AUC of EE. The drug interaction between the contraceptive and colesevelam was decreased when the two drug products were given 4 hours apart.
Substances increasing the plasma concentrations of COCs
Co-administration of atorvastatin or rosuvastatin and certain COCs containing ethinyl estradiol (EE) increase AUC values for EE by approximately 20 to 25%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase plasma EE concentrations, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, or ketoconazole may increase plasma hormone concentrations.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/Hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma concentrations of estrogen and/or progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration with HIV protease inhibitors (decrease [e.g., nelfinavir, ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, (fos)amprenavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, and tipranavir/ritonavir] or increase [e.g., indinavir and atazanavir/ritonavir])/HCV protease inhibitors (decrease [e.g., boceprevir and telaprevir]) or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (decrease [e.g., nevirapine] or increase [e.g., etravirine]).
Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
- COCs containing EE may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds (e.g., cyclosporine, prednisolone, theophylline, tizanidine, and voriconazole) and increase their plasma concentrations.
- COCs have been shown to decrease plasma concentrations of acetaminophen, clofibric acid, morphine, salicylic acid, temazepam and lamotrigine. Significant decrease in plasma concentration of lamotrigine has been shown, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because the serum concentration of thyroid-binding globulin increases with use of COCs.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
The use of contraceptive steroids may influence the results of certain laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors, lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins.
Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)] .
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
There is little or no increased risk of birth defects in women who inadvertently use COCs during early pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or non-genital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb reduction defects) following exposure to low dose COCs prior to conception or during early pregnancy.
Do not administer COCs to induce withdrawal bleeding as a test for pregnancy. Do not use COCs during pregnancy to treat threatened or habitual abortion.
Nursing Mothers
Advise the nursing mother to use other forms of contraception, when possible, until she has weaned her child. COCs can reduce milk production in breastfeeding mothers. This is less likely to occur once breastfeeding is well-established; however, it can occur at any time in some women. Small amounts of oral contraceptive steroids and/or metabolites are present in breast milk.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol have been established in women of reproductive age. Efficacy is expected to be the same for post-pubertal adolescents under the age of 18 and for users 18 years and older. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
There was no significant difference between Tri-Estarylla™ tablets and placebo in mean change in total lumbar spine (L1-L4) and total hip bone mineral density between baseline and Cycle 13 in 123 adolescent females with anorexia nervosa in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, one-year treatment duration clinical trial for the Intent To Treat (ITT) population.
Geriatric Use
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol has not been studied in postmenopausal women and are not indicated in this population.
Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol has not been studied in subjects with hepatic impairment. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with hepatic impairment. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded. [See CONTRAINDICATIONS (4) and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2).]
Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol has not been studied in women with renal impairment.
Overdosage
There have been no reports of serious ill effects from overdosage of oral contraceptives, including ingestion by children. Overdosage may cause withdrawal bleeding in females and nausea.
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol Description
Each of the following products is a combination oral contraceptive containing the progestational compound norgestimate and the estrogenic compound ethinyl estradiol. Norgestimate is designated as (18,19-Dinor-17-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one,17-(acetyloxy)-13-ethyl-, oxime,(17α)-(+)-) and ethinyl estradiol is designated as (19-nor-17α-pregna,1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol).
- Each active white tablet contains 0.18 mg norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol. Inactive ingredients include crospovidone, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, and pregelatinized starch.
- Each active light blue tablet contains 0.215 mg norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol. Inactive ingredients include crospovidone, FD & C Blue No.2 lake, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, and pregelatinized starch
- Each active blue tablet contains 0.25 mg norgestimate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol. Inactive ingredients include crospovidone, FD & C Blue No.2 lake, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, and pregelatinized starch
- Each green tablet contains only inert ingredients, as follows: crospovidone, D &C Yellow No.10 aluminum Lake, FD & C Blue No.2 lake, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, and pregelatinized starch
Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol – Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Oral Contraception COCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation. Other possible mechanisms may include cervical mucus changes that inhibit sperm penetration and endometrial changes that reduce the likelihood of implantation.
- Acne
Acne is a skin condition with a multifactorial etiology, including androgen stimulation of sebum production. While the combination of ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate increases sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and decreases free testosterone, the relationship between these changes and a decrease in the severity of facial acne in otherwise healthy women with this skin condition has not been established.
Pharmacodynamics
No specific pharmacodynamic studies were conducted with Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol.
Pharmacokinetics
Norgestimate (NGM) and EE are rapidly absorbed following oral administration. NGM is rapidly and completely metabolized by first pass (intestinal and/or hepatic) mechanisms to norelgestromin (NGMN) and norgestrel (NG), which are the major active metabolites of norgestimate.
Peak serum concentrations of NGMN and EE are generally reached by 2 hours after administration of norgestimate/ ethinyl estradiol. Accumulation following multiple dosing of the 250 mcg NGM / 35 mcg EE dose is approximately 2-fold for NGMN and EE compared with single dose administration. The pharmacokinetics of NGMN is dose-proportional following NGM doses of 180 mcg to 250 mcg. Steady-state concentration of EE is achieved by Day 7 of each dosing cycle. Steady-state concentrations of NGMN and NG are achieved by Day 21. Non-linear accumulation (approximately 8 fold) of NG is observed as a result of high-affinity binding to SHBG, which limits its biological activity (Table 3).
Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Norgestimate and Ethinyl Estradiol During a Three Cycle Study
Norgestimate-Ethinyl Estradiol – Uses, Side Effects, and More
Do not use this medication if you smoke cigarettes/use tobacco and are over 35 years old. Smoking raises your risk of stroke, heart attack, blood clots, and high blood pressure from hormonal birth control (such as the pill, patch, ring). The risk of these serious problems increases with age and with the number of cigarettes you smoke. Do not smoke or use tobacco.
Warnings:
Do not use this medication if you smoke cigarettes/use tobacco and are over 35 years old. Smoking raises your risk of stroke, heart attack, blood clots, and high blood pressure from hormonal birth control (such as the pill, patch, ring). The risk of these serious problems increases with age and with the number of cigarettes you smoke. Do not smoke or use tobacco.
Uses
This combination hormone medication is used to prevent pregnancy. It contains 2 hormones: a progestin and an estrogen.Besides preventing pregnancy, birth control pills may make your periods more regular, decrease blood loss and painful periods, decrease your risk of ovarian cysts, and also treat acne.Using this medication does not protect you or your partner against sexually transmitted diseases (such as HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia).
How to use Norgestimate-Ethinyl Estradiol
Read the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start using this product and each time you get a refill. The leaflet contains very important information on when to take your pills and what to do if you miss a dose. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once daily. Pick a time of day that is easy for you to remember, and take your pill at the same time each day.
If you are taking the chewable tablet, you may either swallow it whole or chew it thoroughly and swallow. Carefully follow the manufacturer’s directions for your brand.
It is very important to continue taking this medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. With certain brands of birth control pills, the amount of estrogen and progestin in each active tablet will vary at different times in the cycle. It is very important that you follow the package instructions to find the first tablet, start with the first tablet in the pack, and take them in the correct order. Do not skip any doses. Pregnancy is more likely if you miss pills, start a new pack late, or take your pill at a different time of the day than usual.
Vomiting or diarrhea can prevent your birth control pills from working well. If you have vomiting or diarrhea, you may need to use a back-up birth control method (such as condoms, spermicide). Follow the directions in the Patient Information Leaflet and check with your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
Taking this medication after your evening meal or at bedtime may help if you have stomach upset or nausea with the medication. You may choose to take this medication at another time of day that is easier for you to remember. No matter what dosing schedule you use, it is very important that you take this medication at the same time each day, 24 hours apart. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Your pill pack contains 21 pills with active medication. It may also contain 7 reminder pills with no medication. Take one active pill (with hormones) once daily for 21 days in a row. If you are using a product with 28 tablets, take an inactive pill once daily for 7 days in a row after you have taken the last active pill unless otherwise directed by your doctor. If you are using a product with 21 tablets, do not take any tablets for 7 days unless otherwise directed by your doctor. You should have your period during the fourth week of the cycle. After you have taken the last inactive tablet in the pack or gone 7 days without taking an active tablet, start a new pack the next day whether or not you have your period. If you do not get your period, consult your doctor.
If this is the first time you are using this medication and you are not switching from another form of hormonal birth control (such as patch, other birth control pills), take the first tablet in the pack on the first Sunday following the beginning of your menstrual period or on the first day of your period. If your period begins on a Sunday, begin taking this medication on that day. For the first cycle of use only, use an additional form of non-hormonal birth control (such as condoms, spermicide) for the first 7 days to prevent pregnancy until the medication has enough time to work. If you start on the first day of your period, you do not need to use back-up birth control the first week.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about how to switch from other forms of hormonal birth control (such as patch, other birth control pills) to this product. If any information is unclear, consult the Patient Information Leaflet or your doctor or pharmacist.
-





