Many readers are interested in the right subject: medical marijuana in Texas. We are pleased to report that our manufacturer has already done a study of contemporary research on this fascinating subject. They are based on the most up-to-date information. medical We give a wide range of answers to digestion, contemporary research, and sample surveys. Find out more.
For example, marijuana was placed on List I of the Controlled Substances Act of the U.S. Congress in 1977 because “its use is unacceptable.” medical Since then, however, scientific evidence on the use of marijuana has been provided. the medical The superior quality of cannabis has emerged and 23 of the 50 states and DC have developed specific legal cannabis products. medical usage of marijuana LegalTexas has always been reluctant to legalize cannabis, but now the law is changing. More, medical marijuana Texas only allows marijuana for people diagnosed with epilepsy. Find out if you qualify.
Is medicinal marijuana legal in Texas?

On the first day of the week of June 1, 2015, Gov. Greg Abbott Vantexas signed into law a bill under which he legalized the limited introduction of cannabis extracts for robust epilepsy. The new law allows the application of oils equipped with cannabidiol (CBD) to cure stubborn epilepsy. This substance does indeed cause the marijuana plant is not considered euphoric due to the low concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive molecule in cannabis that causes the “high” feelings. The issue and regulation of cannabis oil is checked by the state of Texas, and the oil is only given to epilepsy patients who have previously been given at least two other epilepsy medications; two doctors must approve this new medication before it can be administered to a patient, and the state has not yet approved the new drug.
What is your request for medicinal marijuana in Texas?
For Patients.
Low-THC marijuana It can be granted to patients with specific conditions. Patients must live in Texas every day and be diagnosed with stubborn epilepsy. Additionally, they must have had at least two treatments approved in the past by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that were ineffective. Finally, cannabis oil is only allowed if there are no other good, inexpensive treatments approved by the FDA.
For Medical Professionals
Under the new bills of medical marijuana In Texas, a physician must prescribe marijuana and allow a person to spend a significant portion of his or her time in medical practice evaluating and treating epilepsy. In addition, he or she must be certified in epilepsy or neurology by the South American Council on Psychiatry and Neurology. The superior healing qualities of cannabis must outweigh the risks to the patient.
For example, why do so many people refuse to regulate?
For example, Why Do Numerous People Reject Fresh Regulations of marijuana In Texas, Texas is working elementary with regulations no one can use medical marijuana to some degree.
The distribution and regulation of cannabis oil is checked by the government and this drug is only prescribed to patients who have previously tried at least two normal medications for epilepsy; two doctors must approve the recipe before the patient can get the oil; and the oil must be approved by a physician who is not a doctor.
However, to comply with SB 339, medical professionals must “prescribe” marijuana to their own patients. This means that physicians risk federal criminal sanctions. This is in contrast to DC and the other 23 states that have expanded medical marijuana laws that simply “authorize” or “encourage” physicians to use marijuana. of medical Marijuana. Regulations and certifications are protected by the First Amendment and are federally legal, while recipes are not.
How do other states place medicinal marijuana?
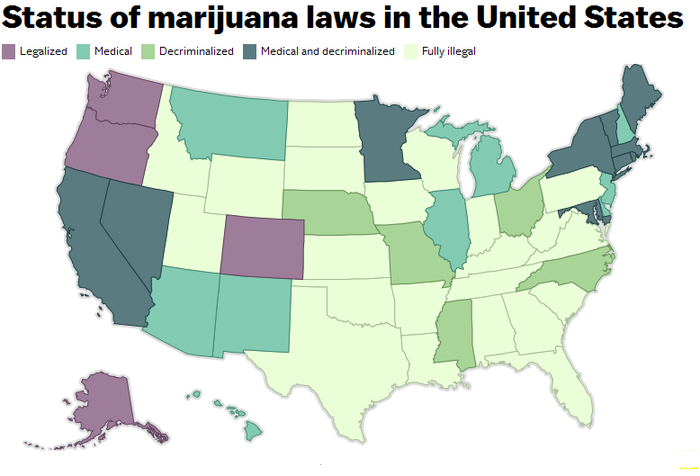
This is an overview of other states where it is legally allowed medical marijuana State laws and restrictions on possession were adopted over the years.
Alaska
Year introduced: 1998.
Limitations on possession: 1 oz. Used; 6 plants (3 adult, immature)
Arizona
Year Approved: 2010
Abundance Limit: 2, 5 oz. Used; 0-12 plants
California
Year Approved: 1996
Population Limit: 8 oz. Used; 6 adults or 12 or more immature plants
Colorado
Year in the past: 2000
Abundance Limit: 2 oz. Used; 6 plants (3 adult, immature)
Connecticut
Year Approved: 2012
Abundance Limit: Moonshine once (exact amount yet to be determined)
District Columbia
Year Approved: 2010
Abundance Limit: 2 oz. Dry; other form limits to be determined
Delaware
Year Approved: 2011
Abundance Limit: 6 oz. Used
Hawaii
Year in the past: 2000
Number Limit: 3 oz. Used; 7 plants (3 adult, immature)
Illinois
Year Approved: 2013
Abundance Limit: 5 oz. of cannabis desired in the direction of 14 days
Maine
Year Approved: 1999
Abundance Limit: 2, 5 oz. Used; 6 plants
Maryland
Year Approved: 2014
Abundance Limit: 30 day inventory, duty amount still to be determined
Massachusetts
Year Approved: 2012
Employee Limit: 60-day face-to-face offer medical use
State of Michigan
Year of Approval: 2008
Population Limit: 2. 5 oz. used; 12 plants
State of Minnesota
Year Approved: 2014
Quantity Limit: Uneven 30-day supply marijuana
State of Montana
Year Approved: (2004)
Quantity Limit: 1 oz. used; 4 plants (mature); 12 seedlings
State of Nevada
Year in the past: 2000
Maximum Quantity: 1 ounce used; 7 plants (3 mature, 4 immature)
New Hampshire
Year Approved: 2013
Limited Quantity: 2 ounces Cannabis desired for a period of 10 days
New Jersey
Year Approved: 2010
Limited Quantity: 2 oz. used
New Mexico
Year of transition: 2007
Maximum Quantity: 6 ounces used; 16 plants (4 mature, 12 immature)
New York
Year Approved: 2014
Supply Limitations: 30-day supply unevenly distributed marijuana
Oregon
Year introduced: 1998.
Allowance Limit: 24 oz used; 24 plants (6 mature, 18 immature)
Rhode Island
Year of Approval: 2006
Density Limit: 2.5 ounces used; 12 plants
Vermont
Year Approved: 2004
Density Limit: 2 oz. used; 9 plants (2 mature, 7 immature)
Washington
Year introduced: 1998.
Quantity Limit: 24 ounces used; 15 plants
Similar Topics
- More info about Ofloxacin and Ornidazole Use
- How long does DABS stay in the system?
- People Who Use Ecstasy: Effects and Dangers
- Smoking Marijuana: Considering the Pros and Cons
- Withdrawal from weed, is it possible?
- Can Marijuana Help Psoriasis?
- Marijuana – What Does It Look Like?
- Is Marijuana Considered Depressing?
- What is it like to get high?
- Cocaine – What is it like in general?
In the same category
- What do you do with methamphetamine?
- What happens if I leak a drug test?
- More info about Ofloxacin and Ornidazole Use
- Can smoking marijuana cause cancer?
- Are there any side effects to very high doses of vitamin B12?
- Street names for marijuana.
- Nicotine-free juice.
- Acute Withdrawal Syndrome






