Many readers are interested in the right subject: medial sacral ligament injuries. Our manufacturer is pleased to report that we have already surveyed contemporary research on this fascinating subject. They are based on the most up-to-date information. medical We give extensive answers to digestion, contemporary research, and sample surveys. Find out more.
The medial collateral ligament is one of the main ligaments On the knee joint. This is on the inside of the knee. Right at the end. the ligament tibia and the other is attached to the femur. It prevents movement of the lateral base of the tibia over the femur when falling forces occur on the knee. Medial collateral ligament injury Occurs during events such as soccer or soccer where there is rapid directional change, rotation and squeezing. Injuries can also occur during skiing and other sports. In other sports there is a lot of motion for stopping and going, weaving and jumping.
What are the signs of a medial collateral zone injury?
Types of Injuries
Injuriesto the medial collateral ligament It can be subdivided into three gradations.
- The most serious degree is considered 1 injury . This means that the ligament Torn but not torn.
- A grade 2 injury means the ligament Partially torn, with some variation in the knee joint.
- The most difficult picture is degree 3 injury . This means your ligament Completely torn and the knee experiences some degree of displacement.
Symptoms.
Symptoms of a medial collateral ligament injury Similar to other knee complaints.
- Can jam or confine the knee joint.
- Sensation that the knee seems to give when weight is placed on it
- Swelling of the knee joint
- Tenderness and pain inside the knee
- When the injury A popping sound when it occurs
- Instability in the knee. This can be a 2nd degree or degree 3 symptom. 3 injury
How was the medial collateral band injured?
Valgusstres Test.
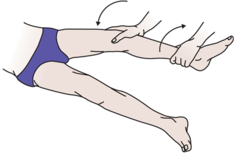
This test is performed with the knee in 30 degree flexion and the leg stolen. Your leg is placed on the edge of the table and the researcher places his or her thighs together in a forceful manner with his or her own. The researcher then applies pressure with one hand on the front lobes of your ankle and places the fingers of the other hand exactly on top to feel the degree of joint opening. The researcher can quantify the general area, i.e., 0-5 mm, 5-10 mm, or an opening greater than 1 cm. This indicates. the injury Soft, small, or difficult.
Radiographic evaluation
Calcification can be tested with X-rays in the early stages. the medial collateral ligament Fieldmri can be ordered for visualization. the ligament Use of T2 weighted images. The researcher can see simultaneous meniscus tears.
How to act in medial collateral ligament injuries?
U.S. Methods
Then try rest, ice, compression, and augmentation in the direction of the first 24 to 72 hours the injury … Take a break from all movements and exercises that cause pain to give the knee time to heal. Initially, use cooling therapy or ice for 10-15 minutes, decreasing frequency as pain decreases. Do not apply ice precisely to the skin. However, use a wet, clean towel or cooling band. Use a knee brace or compression context to protect the joint and reduce swelling. Protect you. injured knee over the hip joint and allow gravity to drain water from the affected area.
Hinged knee brace
For 2nd and 3rd degree injuries, a hinged knee brace is recommended to limit movement and bending of the knee during healing. This has iron details on the sides to help prevent lateral movement.
Electrotherapy
High frequency sound waves are used on the skin during ultrasound. the injured area. Specialists can apply this method to you in the first non-energetic phase of the disease the injury To control pain and swelling. 10 k or interference, electric currents are used in areas around the area to the injury help with swelling and annoying pain.
Bandaging
This can be performed in the initial stages the injury and further in later steps when you return to your own routine. Good immobilization techniques offer a lot of help compared to knee protectors. However, after a while, the tire stretches and must be reapplied to maintain performance.
For a presentation on how to make a harness. the medial collateral , watch this video:
Surgery
It is rare for a medial collateral ligament injury Surgery is required. When is a surgical procedure necessary. the ligament Thus torn, so that it cannot be healed autonomously or in the presence of others ligament Photographic injuries. Arthroscopy (insertion of a small video camera through a small incision by the physician) can qualify the extent of the loss before surgery. injury or other injuries. When. the ligament torn in the thigh or tibial attachment space, the surgeon can reattach using iron screws, bone attachments, giant sutures, or anchors. In the case of a fissure between the tibia and tibia. the ligament Will the surgeon attach them to each other?
Revalidation.
A grade 1 injury A perfect recovery takes 2-6 months; the second and third degree takes 8-12 months.
Rehabilitation includes reinforcement and mobility exercises. All kinds of mobility exercises can be performed to get a completely pain-free range of motion again. Isometric strengthening exercises can be performed in the first steps to prevent muscle atrophy during training. the ligament Heal and retain muscle strength. These exercises such as leg presses, step-ups, and mini-squats can help. However, exercises that require lateral movements and directional configurations should be ignored. Wear a hinged knee brace while performing the exercises.
Initial Steps. the injury Is it a footnote to ignore massage? As the ligament healing, it is possible to apply light cross-friction massage, especially if pain still persists in the later stages of rehabilitation.




