Many readers are interested in the appropriate subject: endometrial thickening: condition, diagnosis and cure. Our manufacturer is pleased to report that we have already conducted a study of current research on the subject that will fascinate you. We provide a wide range of answers based on information from the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and example studies. Keep repeating to find out more.
The endometrium The inner lining of the uterus. Its thickness depends on the woman’s age, reproductive stage, and specific points in the menstrual cycle. A thickened endometrium Depending on the point in any type of woman’s menstrual phase, there may or may not be a normal opening. To determine. endometrial thickening Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used.
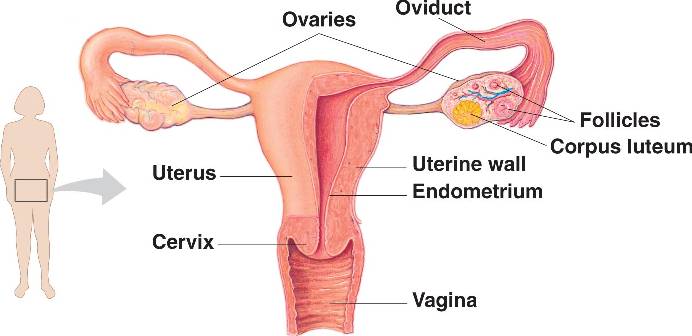
Normal thickness of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle
The endometrium It is common for the thickness and appearance to change during the menstrual cycle. These changes are related to the hormonal changes that occur during the cycle.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, estrogen produced by the ovaries forces the uterus to grow and prepare the uterus for the possibility of pregnancy.
Midway through the cycle, the ovaries release a test round during ovulation. After ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to occur, preparing the fertilized testis for implantation. the endometrium For implantation of the fertilized testis balls. You have the opportunity endometrium thickening At the present time. However, if fertilization does not take place, hormone levels will drop and menstruation will begin. This is the result of the release of uterine adhesions. A new cycle then begins.
What causes a thick uterine lining?
In most cases, endometrium thickening Painful (benign). In addition to the normal changes associated with the menstrual cycle, the hormonal composition of the perimenopausal period still has all the opportunity to cause endometrial thickening Chronic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) still have the opportunity to be associated with fat. endometrium .Aside from these, endometrial Hyperplasia has a greater chance of being associated with uterine cancer.
Symptoms of endometrial thickening This includes abnormal fluctuations in menstrual length, difficult menstrual periods, abnormal intermenstrual bleeding/discharge, or post-transition bleeding. Anemia (layers of blood images) can also be prevented.
Risk factors associated with endometrial thickening include:
- Age >35 yr.
- raspects: white women are more likely to have a blowout.
- Women who have never been pregnant are more likely to have denser skin endometrium
- Your risk increases at older ages.
- Early in life (when menstruation begins)
- Obesity is usually associated with fat endometrium .
- diseases such as diabetes, gallbladder disorders, thyroid disorders, and polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Smoking increases your risk.
- Uterine, Ovarian or Colon Cancer Home Situations
Could you have cancer?
If you are postmenopausal and have an abnormal pregnancy, you need a follow-up exam to see if you are at risk for cancer. thickened endometrium You should undergo a follow-up study to see if you are at risk. for endometrial cancer. The endometrial thickening Often there is estrogen stimulation, which may be related to the use of hormone replacement therapy, or pharmaceutical breast cancer treatments, tamoxifen, or endless estrogen production as a result of obesity. The rarest cause is ovarian tumors that can produce excess estrogen.
Endometrium thickening They can cause bleeding after menopause, but the absence of bleeding does not rule out the possibility of cancer. of endometrial Cancer cannot be ruled out. Proof can be provided by a endometrial Biopsy. The thickness of the intrauterine layer is, endometrial morphology, and a risk point for malignancy when considering endometrial sampling.
diagnosis thickens the endometrium.
Ultrasound of the endometrium can be used as a screening instrument. It can be done during pelvic examination the endometrium taken after dilation and curette are performed. Hysteroscopy can still be performed to look for abnormal areas in the endometrium Fieldone, a delicate device is inserted into the uterus to examine and remove tissue.
Abnormally thick endometrium This can occur for a variety of reasons related to pregnancy. Conditions still have every opportunity to present, based on whether you are considered pre-term or post-menopausal.
Pregnancy-Related Causes
- Early pregnancy (
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Intrauterine blood clots
- Molar pregnancy
- Recent Delivery
- Endometritis
- Abandoned placenta
Causes of Pregnancy
- Endometrial cancer
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrium
- Tamoxifen-related changes
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Endometritis
- Ovarian tumors
How much the endometrium thickens and prevents
- In most cases, treat of endometrial Hyperplasia causes uterine tissue to be removed by dilatation and ring formation (D and C)
- Postmenopausal women who use replacement hormones, leading to repeated endometrial thickening variations, such as progesterone therapy replacement or cessation therapy, should be discussed with their gynecologist.
- Premenopausal women. thickened endometrial Can take oral contraceptives or progesterone with them as indicated endometrial lining.
- Surgical removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) and other reproductive organs is recommended for some women, especially those considered postmenopausal or who do not intend to have children. This reduces the risk of cancer if their situation does not respond to progesterone therapy.
- Endometrial thickening It can also be treated with oral or injectable progestin. It can still be used as a vaginal cloporin via an intraitrin device. Progestin. treatment Can cause vaginal exsanguination, similar to menstrual bleeding.
What can be done to prevent endometrial thickening?
To reduce your risk of thickened endometrium :
- Take progestin/progesteronif you take estrogen after menopause.
- If you menstruate irregularly, take birth control pills with estrogen and progestin.
- Weight loss weight if obese or too heavy. This may decrease risk. of endometrial cancer.






