Many readers are interested in the right subject. It is the difference between dominant and inferior quality. Our manufacturers are happy to say that they have already done research on current studies on this fascinating subject. We will give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating to find out more.
Have you ever wondered why one of your brothers or sisters inherited your mother’s pits? Do you have an acne-free personality like your grandmother while your sister is always taking care of her oily skin? You understand that blue eye genes exist in your family and your mother also has them, but you wonder why you do not have blue eyes. The reality is that physiological characteristics of all kinds are the result of and expression of specific genes. In other words, you must admit that you are more o dominant and recessive traits determined by your genes. Keep repeating to recognize more o
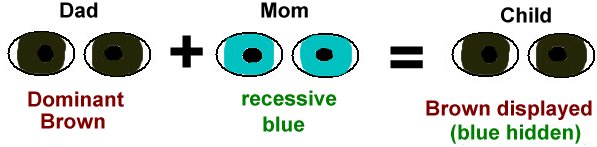
dominant and recessive alleles.
Your genes determine characteristics or traits skin, eyes, hair color, etc. Each gene contains two alleles. One in the mother and one in the founder. Between these two alleles there is one be dominant and the other be recessive . The traits of dominant allele most likely to be expressed, recessive allele, does not express. When a dominant the allele pi a recessive allele, the dominant it takes over and decides if it is an allele or not the traits . These traits In many cases, expression expression and phenotype is clearly expressed and phenotype is called – the genetic code behind the allele is called the genotype. a trait The genotype is called the genotype.
Here’s a friendly example to recognize more about it dominant and recessive traits When it is about eye color, it is the brown eye allele (b) is dominant The blue eye allele (b). is recessive This means that if one of your guardians has blue eyes and the other brown eyes, you are more likely to have brown eyes. In fact, if you have it, it means you have brown eyes! dominant Allellen gets it from both caregivers. If you get it you will still have brown eyes. one recessive allele (b) and one dominant Allele (b). You would only have blue eyes recessive The allele is obtained from both caregivers.
Genetic organization to be determined. the trait The genotype you are said to be homozygous for if you are two recessive or two dominant you have it, you have the allele of your guardian or heterozygous one recessive and one dominant Your caregiver’s allele.
In most cases, if one of your caregivers is a personal contributor, your baby’s brown eyes will be the recessive allele and others. the dominant allele, because dominant The allele contributes another allele. Sometimes both caregivers have brown eyes, but they donate their personal alleles. the recessive alleles, and eventually the baby will have blue eyes. While owning appearance is important, genetic inheritance is not always so fundamental.
Gender-related inheritance
If you want to know more about … dominant and recessive traits It is very important to know more about gender inheritance. To begin with, it is good for the nobility.
- Females have 2 x chromosomes, while males have 1 x and 1 chromosome.
- The X chromosome contains many genes that are inherited with it.
- The X chromosome comes from the mother when it is a boy and from the mother or founder when it is a female.
This means that a male has only one allele on the X-binding gene, while a female has two. Discrepancies in all of these sex genes can lead to genetic abnormalities that can lead to diseases such as hemophilia. This disease only affects women of the period who have two copies of the of recessive alleles from all caregivers. Since males are affected on the 1 x chromosome, only one copy of the hemophiliac is sufficient to cause the disease. That is why hemophilia is much more common in males.
List of dominant and recessive traits
Here is a list of some of the most common dominant and recessive traits .
Dominant features
recessive properties
Eye color
Green, gray, blue, brown eyes
Her
Non-red hair, black hair, curly hair.
Hair
Light, blonde, steep, reddish hair.
Vision.
Night blindness, color blindness;.
Facial features
Appendix.
Toes, minor toes, short toes, tuber toes, fingers
Other.
Normal pigmented skin.
Immunity to poisoning by Ivy;.
Normal hearing; Normal speech; Normal
Normal blood coagulation;.
Susceptibility to poisoning by Ivy;.
Deaf mutism, spontaneous deafness;.






