Many readers are interested in the appropriate subject: chemical burns. Our makers are pleased to report that they have already done modern research studies on the subject that will fascinate you. We will give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers and sample surveys. Find out more.
First Aid
Chemicals
Chemical burns he injury of the skin, eyes, mouth, or internal organs caused by contact with a corrosive substance. Sometimes called corrosive burns. burns .
Chemical burns They can occur at home, at work, or at school. They can happen in tragedies or attacks. However, few people in the U.S. have died after coming in contact with these chemicals. chemicals At home, almost all known drugs can cause serious damage to homes and storage spaces.
Many chemical burns Not because of accidental use of products such as hair, skin, and nail care. However, there is a risk of injury in the home and save a chemical burn more in the workplace, especially in companies and production plants where huge values are used. of chemicals .
Types of chemical burns
Chemical burns They are classified as other burns Based on the amount of damage caused:
- Superficial or 1st degree. burns Affects only the outer layer of the skin, the epidermis. Area is red and painful, but usually no permanent damage.
- Partial thickness or 2 degrees burns Extends to the second skin layer, the leather skin. There is a chance of blistering and swelling, but also a chance to forget the scar.
- Full thickness or 3rd degree burns There is a good chance of going through the skin and destroying the underlying tissue. This area has a chance to appear black or white. Nerves are destroyed and may not be painful.
Chemical conditions of burns and risk points.
Most chemicals that cause burns Either strong acid or cause. See physician’s information on hazard labels. chemicals Check for expected toxicity. Precautions and buyer information have every opportunity to lower the risk of family injury. Different family products can cause chemical burns , including:
- Ammonia
- Batteries
- Bleaching
- Concrete mix
- Rinsing and toilet cleaners
- Metal cleaners
- Block binder
- Dental supplies
Infants and the elderly are at greater risk for burns . Chemical burns tend to happen to:
- Young infants are exploring their environment and taking risks
- People in contact with slaves chemicals
Chemical signs of burns
Chemical burn of the skin.
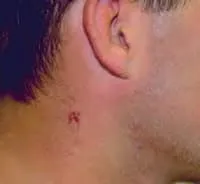
Chemical burn of the eye.
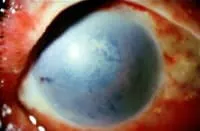
All chemical burns must be considered a necessary medical emergency. If you are a chemical burn By mouth or throat, call 911 for immediate medical assistance.
Most chemical burns Occurs on face, eyes, arms, and legs. Commonly. a chemical burn usually relatively small and require only outpatient treatment. Chemicals burns However, it can be. Some agents have every opportunity to cause thorough tissue damage as well as refute it the first time they see it.
Signs and symptoms of chemical burns These include
- Redness, discomfort, or burning sensation in the contact area
- Pain or numbness in the contact area
- Blistering or dark skin in the contact area
- Vision changes if the chemical gets into your eyes
- Coughing or shortness of breath
Tissue damage from chemical burns To what degree, depending on a variety of things:
- Power or concentration the chemical
- Place of contact (eyes, skin, mucous membranes)
- Absorption or inhalation
- Shell is intact
- How much of the chemical You came in contact
- Duration of exposure
- How the chemical works
If harmful, you can create each right
- Hypotension
- Tear, impotence, dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Headache
- muscle
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Cardiac arrest
- Chemical burns May be very busy Dead. a chemical The rarest as well as the most traumatic can occur.
size of medical emergency assistance in chemical burns.
Any chemical burn May be a legitimate reason to seek medical assistance immediately. If you are unsure how serious the injury is, or if the person is not medically stable, always call 911. Also call 911 if you are concerned about the injury or if the person is not medically stable. a chemical injury.
Rescuers are trained to assess the severity of injuries. a chemical burn Begin treatment and transport the patient to a clinic.
Care providers can still assess whether both you and the area of tragedy need to be disinfected before going to the clinic; when contacting 911, provide the operator with as much correct information as possible.
- How many people were injured and where they are located
- How the injuries were created
- Whether care providers can reach the victim or if the victim is trapped
- Name, power, size or quantity the chemical causing the burn (give the container). the chemical (perhaps for the care provider).
- Duration of contact with the chemical
Always find the help you need any burn Diameter is more than 3 inches or very deep. Also, seek help urgently any chemical burns If it involves the person, eye, gro diameter, arm, leg, or buttocks or is on a joint.
Even if the exposure is very small and you have received major first aid, you should still ask your own physician to treat the injury and the chemical involved and a small dose after treatment is not necessary. Your doctor can provide the correct treatment or refer you to the health center’s emergency department. If you are a person with the burn Ask your own doctor if you need a shot of tetanus.
Chemical diagnosis of burns
Emergency department can wait for a good diagnosis:
- Initial evaluation and stabilization
- Rapid evaluation of the chemical
- Determination of the extent of the injury
- Blood work and other tests to determine if the patient should be admitted to the hospital.
Most people with chemical burns Do not need to be included. Most people can go home after seeking further help with their doctor. In extreme cases, however, a person may need to be admitted to a clinic.
Treatment of Chemical Burns
As soon as you or your baby talk about a dangerous chemical burn. chemical Start first aid. If you are unsure, call Anti-IGIF Services at 800-222-1222. the chemical is toxic.
If you slowly suffer an injury, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or other signs throughout the trunk, call 911 immediately. If you can help an affected person who is having these symptoms, cancel that person and call 911 immediately.
First Aid
- Remove yourself or with help the burn from the tragedy area.
- Remove all soiled clothing.
- Wash the affected area and dilute or remove the substance with copious amounts of water. Wash for at least 20 minutes, making sure the rinse does not come in contact with unapplied body parts. Gently scrub the hard material, again avoiding poor body parts.
- Especially wash away any chemical With your eyes or a person’s eyes. Sometimes a shower is the best way to get lots of water to your eyes.
MEDICAL
- IV water is obligatory for clitches and decreases the frequency of cardiac arrhythmias.
- IV access can still be used for medical care, which is important for healing pain or defense against infection.
- Decontamination (possibly irrigation with water) begins.
- You get an antidote to prevent it the chemical , if appropriate.
- In many cases, antibiotics are not needed for minors. chemical burns .
- The wound is cleaned and connected to a sterile wrap with pharmaceutical cream if needed.
- Consultations with other medical professionals will probably take place.
- Pain from a burn Often can be violent. Appropriate pain control will be assessed by your physician.
- If there are symptoms of breathing problems, you may be helped by placement of a ventilation tube in the airway.
- If necessary, a tetanus booster will be given.
- Itching as a burn Healing can be a discouraging task. Maybe you need special medications to take it away.
- For severe burns Maybe you need surgery. In a process called skin grafting, a piece of healthy skin can be transplanted from somewhere else on the body or from a donor to replace broken skin.
- Cosmetic or reconstructive surgery may be needed to combat scarring.
- Physical and competent treatment can prevent scars from limiting the range of motion.
- Counseling and Support Groups Help with Sensory Challenges Due to Trauma and Interest
Follow-up care for chemical burn s-up care
Call your own physician within 24 hours of leaving the emergency department to arrange for follow-up aftercare. If there are new difficulties or challenges, rather call
Chemical aggravation of burns
Serious chemical burns Can cause long-term aggravation:
- Many people experience pain and scarring.
- Burning eyes can lead to blindness.
- Swallowing harmful chemicals Can cause problems in the digestive tract, which can lead to permanent disability.
- Some acid burns Can lead to loss of fingers and toes.
- Burns can cause sensory problems, including fear, depression, and insomnia.
Prevent chemical burns.
- Secure all chemicals Inside and outside the home in closed cupboards or out of reach of children.
- Store chemicals In their own packaging.
- Try to use chemicals Use as little as possible and do not let them come in contact with your skin.
- When using chemicals Always follow the manufacturer’s label directions and precautions.
- Ensure work area is well ventilated.
- Wear non-toxic clothing and eye protection: remember: safety first!
Property Chemical Burns
Most chemical burns secondary important and can be handled without causing long-term problems. Some burns however, cause significant wounds and other medical aggravation.
Sources indicate that
EmedicineHealth: “chemical burns”.
Mayo Clinic: “Chemical burns : first support, “Burns”.
Merck Manual: “Chemical Combustion”, “Burns”.
Statpearls: “Chemical Combustion”.
Surgical Journal: “Bite”. burn caused by intracutaneous autonomously generated hydrochloric acid for suicide crawling: adequate wound healing and active recovery in nonsurgical treatment”.
Johns Hopkins Medicine: “Burns and Wounds”.
American Dental Connection: “Teeth whitening/bleaching: healing advice for dentists and their patients”.
International Journal of Millecr Science: “Then the Pearlite Was Burned”.
National Health Service: “Acid and chemical burns .”
New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Med Midden: “Burning Security and Prevention”.
Department of Health and Community Services: “Effects of Skin Contact with Chemicals”.
Chemicals
Chemical burns Can occur when in contact with aggressive substances such as bleach, battery acid, antiseptics, etc. People they work with chemicals They assume more risk because of their work of chemical burns Field infants are still at risk because they are more likely to accidentally touch or swallow household items. chemicals .
- Assignment 216.444.5725
- Meetings and Locations
- Request an Appointment
JUDGEMENT.
What is a chemical burn ?
A chemical burn Damage to body tissues due to aggressive or corrosive medications. This can be get chemical burns from your skin, eyes, or inside your body. Most likely chemical burns the result of an accidental spill. a chemical By yourself. But you can still swallow it chemicals or become familiar with it in other ways.
Chemical burns They range from mild to severe. Mild. chemical burns Usually heals quickly, but serious chemical burns Can cause systematic tissue damage, scarring, or death. Chemical. burns Requires immediate healing.
Who’s at risk for chemical burns ?
All persons working with chemicals is at risk for chemical burns , including:
- Construction workers.
- Factory workers.
- Farmers.
- Laboratory technicians.
- Mechanics.
- Military.
- Plumbers.
It is important to note that babies (especially infants) are at the greatest risk for burns Caused by household chemical Groceries. They can accidentally touch or swallow detergent, bleach, or cleaning products.
How common are chemical burns ?
In the period from 2005 to 2014, within 3% of all adults were found to be to burn centers in the U.S. had chemical burns One study showed that in the direction of 17 years old, 40, 000 children (or 2, 300 children per year) were admitted to the emergency department a chemical burn From Home Cleaning Agents.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes chemical burns ?
When harsh chemicals When they come in contact with your skin, eyes, or other tissues of your body, they have every opportunity to eradicate the cells. Evil has the ability to overcome the superficial layers of skin or tissue and cause deep damage. Chemicals burns can be much more serious than heat damage. burns Chemicals often sit on the skin for a long time and eat tissue.
There are a number of medications that one has a chance of chemical burns Some of the more popular ones are
- Battery acid.
- Bleaching.
- Determinants.
- Cleaning agents.
- Fertilizers.
- Hair relaxants.
- Cleaning methods for metal and rust removers.
- Paints.
- Pesticides.
- Disinfectants and antiseptics.
- Swimming pool chemicals .
- Cleaning agents for toilets.
- Wet cement.
What symptoms of chemical burns ?
Chemical burns Can cause on the skin:
- Blisters or crusting.
- Cracked, dry skin.
- Soreness.
- Removal of skin.
- Redness.
- Skin discoloration.
- Swelling.
Chemical burns Your eyes may develop
- Blurred vision.
- Swelling of the eyelids.
- Soreness.
- Redness.
- Blocking or burning.
- Watery eyes.
- Blindness (if such is the case).
Chemical burns Of the way (swallowing) may include
- Chest pain.
- Cough.
- Difficulty in speaking (Dysfonie).
- Drooling.
- Ho respect.
- Low blood pressure (hypotension).
- Nausea and vomiting or blood nausea.
- Sore mouth or throat (especially when swallowing).
- Perforation (hole) in the stomach, digestive tract (tube connecting the stomach to the throat), or cornea (outer lens of the eye).
- Dyspneu (shortness of breath).
- Swelling of the upper airway (edema).
Diagnosis and Testing
How are chemical burns diagnosed?
Usually, the care provider can make a diagnosis chemical burns skin to know the size, depth, and other characteristics of the skin. the burn They can also use other tests to make a diagnosis burns on your skin, in your eyes, or swallowed. a chemical , including:
- Blood test: swallow chemicals may affect the way your organs work. You can still chemicals Absorb it into your body through your skin eye burns Field Health care providers can perform CBCs and other laboratory tests to examine a variety of functions, including kidney, liver, nonthreshold function, and metabolic function. of chemical burn .
- Endoscopy: When swallowed. a chemical An endoscopic evaluation may be necessary. During an upper endoscopy, the physician uses a thin, flexible tube (endoscope) with a camera on one end. The physician guides the tube to the recipient and passes it through the digestive tract. A video monitor displays images of the throat, digestive tract, and stomach. They are likely to check for the following for burn damaged tissue.
- Eye care: An ophthalmologist or optometrist will examine your eyes. chemical burns your eyes. They will immediately flush your eyes with water. They will then identify symptoms and analyze the depth of vision. the burn They may also place certain dyes in your eye to locate areas of collapsed tissue.
- Visualization: visualization studies help identify internal body damage caused by swallowing. a chemical You may undergo a chest x-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan to help identify internal tissue damage. You may undergo a chest x-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan to help identify internal tissue damage.
Treatment
How are chemical burns treated?
Chemical burns You need immediate medical attention. call 911 and do the following
- Remove clothing. Use gloves to protect your hands. Cut off contaminated clothing. the chemical Avoid contact with other parts of the body.
- Remove the chemical : While wearing gloves, brush off any other dry traces. the chemical , but don’t wipe the chemical Step away. Wiping may spread contamination to other parts of the skin.
- Rinse with water: rinse the burned area from the skin or with cold water. Continue rinsing for at least 30 minutes. as chemicals May continue to destroy skin after contact. Do not allow contaminated water to touch other areas of the skin. There are. chemicals Do not wash feet in water containing coal acid, oxybenzene, sulfuric acid, dry powder, or iron compounds.
- DRINK WATER: If substance is swallowed, drink water. a chemical dust, drink water to dilute it in the stomach. Do not take anything to relieve yourself. vomiting and diarrhea. a chemical This substance can cause the most damage when it passes through the digestive tract.
Then go to a health center; South American Burns Connection advises anyone with symptoms to a chemical burn should seek care at a burn Contact the center immediately or call the State Poison Line hot section (1-800-222-1222) for treatment information. A burn The center is part of the following specialty outpatient clinics to burn Concerns. If you go to an urgent care facility, you will probably be referred to the center. a burn center.
Once you arrive at the clinic, your medical team will
- Your burden is to burn .
- Continue rinsing. burn .
- If you feel any discomfort, anesthesia will be administered.
- Lubricate the skin medications to prevent infection. Or they give it to you through a vein in your arm.
- Dry dressing or compress into a soft or medium context burns .
If you have a serious burn You may need surgery to remove burnt areas of skin. Some people need skin grafts. The surgeon will take healthy skin from other parts of your body and stick it to the burnt area. Surgery can still restore perforation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
Are chemical burns preventable?
Reduce your risk of chemical burns Take the right precautions:
- Use other products that are not so sharp.
- Keep chemicals Keep them in protective packaging.
- Know what chemicals You are working at their risk.
- Store chemicals In a harmless space not cheap for children.
- Wear protective clothing and equipment such as gloves, safety glasses and facial screens.
Outlook
What are the prospects of people with chemical burns ?
Most mild chemical burns Healing without permanent scarring. However, the long-term consequences are serious chemical burns may include:
- Skin cancer, stomach or gastrointestinal tract.
- Stenosis of the alimentary canal (narrowing of the alimentary canal, sometimes due to scarring).
- Perforation (hole) in the stomach, digestive tract, or cornea.
- Scars.
- Skin discoloration.
- Loss of vision.
Living with
When should I consult a doctor? a chemical burn ?
Seek help immediately for all types of of chemical burn . If you have a burn recovery and contact your doctor as it the burn :
- Causes severe pain.
- Has yellow or green discharge
- Becomes more severe.
- Seems to be infected.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
You can ask your own doctor these questions.
- Is there a long-term surcharge for long-term infection? a chemical burn ?
- How can I reduce my risk of such infections and scarring? the chemical burn heals?
- How severe is the chemical burn ?
- How can I get my risk a chemical burn in the future?
Note from Cleveland Clinic.
Chemical burns You can act if you work with chemicals or other heavy medications for your work. People, especially young children, can receive notes from the Cleveland Clinic get chemical burns If they accidentally touch or swallow certain household items. chemicals You should seek medical assistance from your health care provider. any chemical burn You must seek medical assistance from your care provider even if they seem slippery. As opposed to heat. burns , chemical burns Can continue to cause tissue damage even after you come in contact with it. Specific healing is required to prevent scarring and other complications.
Chemical and Acid Burns
Christina Donnelly is a freelance fiction writer and editor who has worked extensively with wells and science. In real time, she works as content at Anthem Health.
Updated February 28, 2022
Michael Menna is considered a board-certified intensive care physician in the emergency department at the White Plains Clinic in White Plains, NY.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chemical burns – Also called corrosive burns -О. Cakr occurs when the skin comes into contact with acids, bases, alkalis, detergents, solvents, or fumes generated by these corrosive substances. It usually affects the eyes, face, hands, and feet, but can cause serious damage to the mouth and throat if the corrosive substance leaks.
Fortunately, most chemical burns It does not cause serious skin damage. Most cases are caused by common household or workplace materials and can be treated on an outpatient basis; only 5% of patients require emergency treatment. a chemical burn They are admitted to the clinic. However, highly corrosive materials can destroy the deepest layers of tissue, and the damage is not always immediately ruled out.
This is because materials are chemical burns so common in homes, schools, and workplaces, it is essential to know what to do if you, a loved one, or a co-worker comes in contact with a corrosive material.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chemical-burns-symptoms-causes-diagnosis-treatment-4174243-5bb7be3346e0fb002691d776.png)
Symptoms of Chemical Burns
The symptoms of a chemical burn It depends on several important things.
- What substance caused the injury. the chemical burn
- Where the fabric came in contact with the actual tissue
- How long the material has been exposed to the corrosive substance
- Whether the substance was inhaled or swallowed
For example, bleach in contact with the skin and bleach in contact with the eyes can have very different effects.
Symptoms vary, but common signs and symptoms include a chemical burn include:
- Pain, redness, discomfort, burning or numbness at the contact area
- Blistering or dead, blackened skin at the contact area
- Blurred vision or complete blindness if the substance comes in contact with the eyes
- Coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath if the substance is inhaled or swallowed
In very severe chemical burns Or if a corrosive substance is swallowed, the following symptoms may occur
- Weakness, dizziness, fainting
- Headache
- Muscle cramps or spasms.
- Low blood pressure, arrhythmia, and even cardiac arrest.
If you, a loved one, or a co-worker comes into contact with a corrosive substance, seek medical attention immediately. Even if the exposure appears minor, such as a splash on your hand, call your health care provider or poison control center to determine if appropriate treatment is needed.
If a corrosive substance is swallowed or, the chemical burn very deep, greater than 5 cm in width, or affecting the eyes, face, groin, buttocks, or joints, seek medical attention immediately.
Causes
Chemical burns They can occur in any room where you work with corrosive and corrosive materials – usually caused by acids or in homes, workplaces, and schools. Chemicals burns Everyone can meet, but those working in production facilities, children, and the elderly are at a higher risk of injury.
Some similar products likely to cause the following chemical burns include:
- Bleach, ammonia, drain cleaners, and other everyday cleaning methods
- Skin, hair, nail care products, and teeth bleach
- Car batteries
- Chlorine in swimming pools and swimming pool cleaning systems
If possible, read warnings and physician information about corrosive product labels before starting. Often the information and subsequent implementation to the customer can prevent serious medical problems.
Although most chemical burns Corrosive products can be used in attacks, even when misused incorrectly. Attacks with corrosive products are more common in women worldwide.
Diagnosis
Like symptoms of a chemical burn The care provider performs a physical examination to assess direct tissue damage caused by the injury. The physician performs a physical examination to assess direct tissue damage caused by the injury. the chemical burn Then ask a series of questions to assess possible damage. You should inform your own health care provider about the causative agent(s) that caused the injury. the chemical burn The length of time he or she has been in contact with the skin and the affected body part.
If you have a serious chemical burn If your care provider can perform blood tests to determine if transport to a clinic is necessary.
After physiologic examination and interview, the chemical burn These burns are labeled as follows
- First or superficial burns: these types of burns affect only the epidermis or outer layer of the skin. Mild discoloration of the skin is considered a very frequent sign of a first degree burn. burn .
- Second-degree or selective thickness of burn: This affects the epidermis and dermis (second) layers of the skin. burns It can be very red, inflamed, painful, and may leave.
- Third degree or absolute thickness of the burn: nonsense, this burns causes extensive damage to the epidermis and leather skin, as well as to the bone, tendon, muscle and nerve endings.
Your care provider will advise you of your healing options based on your category. chemical burns .
Chemical and Acidity Treatment
Typically, chemical burns No urgent need for hospitalization or special treatment
For a minor chemical burn Basic first aid can relieve pain and tissue damage When treating minors chemical burn , be sure to:
- Remove yourself, a loved one, or a co-worker from the tragedy.
- Remove all soiled clothing.
- Wash affected objects with water for at least 20 minutes.
- Remove all objects of any kind from the affected area.
After the first support is in place, chemical burns you will need to speak to your own care provider about your upcoming care.
If you or someone else is affected a chemical burn dizziness, creaky breathing, difficulty breathing, or other slow symptoms begin, call 112 immediately.
Some ways to heal seriously chemical burns include:
- IV water to regulate heart rate and blood pressure, or intravenous substances or medications to heal pain or prevent infection
- Antidotes to prevent the effects of corrosive substances
- Professional cleaning and beating
- IV Intravenous or other anesthetic to control annoying pain
- Tetanus booster to prevent bacterial infection
Chemical burns Although rarely fatal, it is essential to take the necessary steps to prevent infection and to protect and treat damaged tissue. If you are treated a chemical burn within 24 hours of injury, it is most important to organize follow-up help from your care provider.
If you are in very
Chemical and acid burns potentially painful, but the good news is that most of these products can be touched with lead 1 support and further care. When using corrosive or corrosive products, it is imperative to read all possible warning labels and use help to avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mouth. In many cases, the buyer’s correct information can prevent a serious and necessary medical history.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to approach whitewasher burn ?
You need to bleach it burn like most other chemical burns – Move to a non-toxic space and remove all clothing and accessories. the burn Then run cold water for 20 minutes. When. the burn it can be folded, you can carefully fill it with stromberry or cream and place the gauze on top. It is recommended that you consult your medical supplier about bleach burn Even after home treatment. This is even more important if it comes through joints or swallowing, eyes, hands, genitals, scalp, or swallowing.
Should a mild chemical burn Will you be taken to the hospital?
If a mild chemical burn The following healing has been received and the substance it caused identified, the burn It may not be necessary to bring it to the clinic. However, the care provider should be notified in case they attempt to contact themselves. Even if they do. the burn it does not seem important, there is no harm in sorting this out. When. the chemical burn Any kind of symptoms of infection, such as swelling, suspension, redness, fever, etc.
How long does a chemical burn take to heal?
- First-degree burn Usually it heals in the direction of 3 to 6 days; after a day or two, the peel may shed a little.
- Second-degree burn Healing may take 3 months or more. The severity of this of burn affects the top layer of skin and part of the layer below it.
- Third and fourth levels burn Skin grafting may be required. This is a procedure in which healthy skin is sutured to the shattered area to aid in skin repair. burn . Severe burns This may require a skin graft, a procedure in which healthy skin is sutured to the shattered area to aid in skin repair.
Very happy people enjoy only quality information from that quantity of peer-reviewed research to help set a precedent for our notes. Read about our editorial process to learn more about how we set precedents and keep our content clear and credible.
- Nemours Kid Sheet. Burns
- Medline Plus. Minor burns – aftercare.
Read more
- Johns Hopkins Medical Book Depository. Burns.
- Mayo Clinic. Chemical burns: first aid.
- Medscape. Chemical burns.
Christina Donnelly Christina Donnelly is a freelance fiction writer and editor who covers a wide range of wellness and science table of contents. She works as content material for Anthem Health. & lt; plan& gt;: This may take several months to occur.






