Many readers are interested in the appropriate subjects: conditions for BNP increase and information on BNP testing. I am pleased to report that our manufacturer is already investigating current research about subject you are interested in. Based on the information the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys, we can give you a wide range of answers. Keep repeating to find out more.
BNP, or brain natriuretic peptide, is a hormone produced by the heart and identified in the blood It is isolated as a result of abnormal elongation of the myocardium. Its value is considered an indicator of the state of the psychovascular system and is known to be regarded as a great support in diagnosing the severity of cardiac deficiencies and criteria such as diastolic dysfunction. As a rule, though, the amount of this hormone present in our blood is always low, an elevated BNP, however, is far from normal.
Causes of increased BNP
1. cardiac causes
- Heart failure
- Diastolic dysfunction
- Hypertension combined with left ventricular hypertrophy
- Acute coronary syndrome is a term used to describe a number of heart diseases, including myocardial infarction and angina pectoris.
- Arrhythmia
- 1. heart valve disease (mitral valve subsidence, aortic stem)
2. non-cardiac causes
- Primary or secondary pulmonary hypertension
- Non-optional – vascular occlusion of pulmonary embolism
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is associated with inadequate breathing and lung
- Excessive thyroid – hyperthyroidism
- Septicemia
- Chronic and acute kidney damage
- Water and sodium retention caused by medications (Avandia®, Actos®, etc.)
- Water and sodium retention caused by failing kidneys
Use of the GNP Test
We now know the cause of elevated BNP, what can the BNP test be used for?
1. heart failure
The BNP test is very useful in diagnosing heart failure. It can help determine if a patient needs an echocardiogram and can help determine if a patient’s already-treated regimen needs to be adjusted for heart failure.
- BNP analysis indicates the presence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction, which minimally limits the number of people who require an echocardiogram.
- BNP values are compatible with specific power scales in line with the New York Heart Association’s (NYHA) systematization of cardiac defects and in line with potential work.
- Due to the low amount of this hormone, heart deficiency may be disabling, but a very large amount of heart approves the probability of heart deficiency. However, if there are intervening values in GNP values, supplemental investigations are required.
- BNP testing can help triage patients with signs of cardiac deficiency and screen those at highest risk for cardiac deficiency.
- Various preparatory studies have shown that BNP concentrations of all species can help distinguish between pulmonary disease and cardiac compensation.
- Another preparatory study demonstrated that analysis of BNP in bunter meat helps qualify the burden and possible risk of cardiac deficiency.
This study showed that BNP values correlated strongly with these results.
- The better results were for patients whose GDP values decreased during their stay at the clinic.
- Patients who were killed in the clinic or dismissed within one month of their dismissal had either a slight decrease in GNP values or an increase in BNP degrees.
- The last BNP measurement for a dismissal in the clinic was a more reliable moment to predict the outcome.
2 Other clinical applications
- Causes of elevated BNP is not necessarily associated with cardiac deficiency. Its increased value is also known to predict death and psychological vascular disease, possibly in people without heart deficiency.
- Evaluation of BNP can help recognize patients at risk for cardiac rhythm disorders and heart attacks.
- Natriuretic peptide is considered a strong indicator of mortality in people suffering from acute, annoying chest pain.
- It plays a major role in predicting mortality from cerebrovascular tragedies.
Information about the BNP test
1. when is the GNP test performed?
Physicians like to order a GNP or NT-PROBNP analysis when a patient is showing corresponding signs of cardiac deficiency.
- Fatigue
- Dyspnea or respiratory distress
- Swelling in the abdomen and lower part of the body (feet, ankles, legs)
If someone is suffering from signs of cardiac deficiency that urgently require a quick diagnosis, testing can be performed in the emergency department.
The GNP or NT-PROBNP test is performed for a random number of months while the patient undergoes cardiac deficiency therapy to test its effectiveness.
2. how to prepare for the GNP test?
Do not eat lunch; do not drink anything but water except for 8-12 hours for the GNP test. Pay attention to your doctor’s instructions and stop taking any heart medications before you do the test. Don’t be shy about talking to your own doctor. about 2. the problems you are having with the test, including the need, risks, procedure, and results.
3. how it is done.
The medical employee taking your blood will take care of the good stuff:
- Wrap the shoulder by stopping the individual’s blood flow through the elastic.
- Clean the puncture site with a small amount of alcohol.
- Pierce the tubing with the needle in the vein and fill it with blood.
- Remove the strip from the arm to collect the bloodstream and absorb the required amount of blood.
- Immediately after removing the needle, place a piece of cotton wool over the puncture site.
4 Interpretation of BNP test results
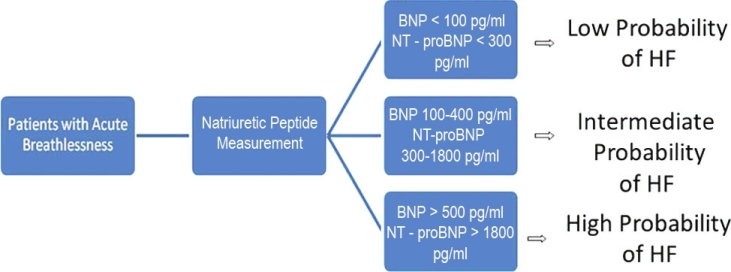
Given the precedent, there are many reasons for this of elevated BNP can be a difficult course to read the value of the brain chemistry peptide. Nonetheless, all physicians consider the two values of interpretation. It rules out heart deficiency as a possible cause, and higher values rule out and indicate that there is life.
If the value of BNP is less than 100 pg/mL, the possibility of cardiac deficiency is ruled out. At the same time, a value 400 pg/mL or higher means a 95% chance of cardiac deficiency. Intermediate values vary from 100 pg/ml to 400 pg/ml, and if the test produces such a value, additional testing is required; BNP can still be found in the blood, and the normal spectrum varies from 0, 5 pg/ml to 30 pg/ml.