Many readers are interested in the right subject: can MRSA cure everything? Our makers are pleased to have already researched current studies on this fascinating subject. We will give you a broad answer based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating to find out more.
MRSA, or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, can be called a variety of staphylococci resistant to compound drugs used to treat staphylococci. Over the years, due to unnecessary use of microorganisms and genetic mutations in the microorganisms, to some extent, some strains of microben have become resistant to the drugs. In general, only a fairly small percentage of the population (1%) are carriers of the MRSA tribe.
Healthy individuals (30%) carry Staphylococcus aureus in their nasal passages and on their skin, which usually does not cause infection. However, when the bacteria penetrate the body through cracks or cut into the skin, infection can occur, although MRSA is more difficult to cure than most tribes of Staphylococcus aureus. completely ? The point is that if MRSA is not treated promptly, the condition can lead to sepsis and death.
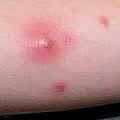
Types of MRSA
There are two systematizations of community acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) and clinically acquired MRSA (HA-MRSA).
CA-MRSA.
Contracted MRSA infections are found in a community of healthy people who have not received medical intervention or have been admitted to a hospital in the past year. Anyone can acquire CA-MRSA through direct contact with an infected wound or through personal contact with an infected person. Poor hygiene can easily spread the bacteria and outbreak by injecting groups of drug users, athletes, prisoners, guests, and other groups living in busy situations because of inaccessibility or inadequate hand washing.
HA-MRSA
Hospital-acquired infections (HA-MRSA) occur in people who have recently been admitted to a hospital, had surgery or dialysis, or have been in a care institution for a long time in the past 6 months. This also applies to people who recently had a residential catheter, intravenous catheter, or another medical device at the time of reproduction. Direct contact with poorly disinfected surgical instruments, dirty hands, or soiled linens can result in infection with HA-MRSA. This can lead to serious health problems such as blood infections and pneumonia.
Can MRSA be completely cured?
The good news is: yes. Yes, but MRSA is not easy to cure and is resistant to almost all medications. Decolonization and some medications can cure MRSA infection. Routine treatment can consist of washing the entire body with chlorhexidine gargle drug, mupirocin nasal ointment, and chlorhexidine soap for 5 days. Urinary and intestinal colonies are treated with vancomycin (oral) and sulfonamides such as cotrimoxazole. Vaginal colonies are treated with otopidine. For ineffective treatment, other medications can be added to the treatment. Successful decolonization is achieved when the results are negative in three different sets of growths and the standardized MRSA colonization program is very effective in those who have completed the full treatment.
How else is MRSA treated?
People with skin infections can be tested by MRSA propagation, and results are usually available within two to three days. However, people with infections of internal organs such as bones and joints usually require blood tests combined with imaging such as computed tomography (CT) scans, x-rays, and echocardiograms. If the diagnosis is confirmed, antibiotics are usually prescribed and the dose or pattern can be changed if culture results are available.
Can MRSA be prevented?
Again, MRSA cannot be cured. completely It can be prevented. With proper measurement, you can reduce the risk of increasing or distributing CA-MRSA infections.
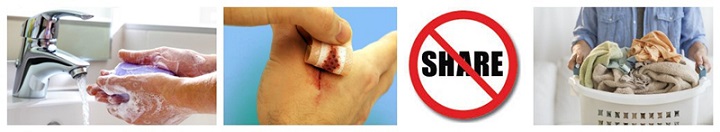
- Wash your hands: the most important thing you can do is good hygiene by washing your hands regularly. This is the most effective way to prevent the spread of MRSA. Begin by carefully brushing your hands for at least 20 seconds before drying them with a clean, unused towel. Use another clean towel to prevent tapping. Health professionals recommend using a hand mold device containing 60% alcohol.
- Use of bandages: Every day you want to prevent skin rashes of all kinds. The use of a connection also protects against the possibility of infection or other fluids, including Staphylococcus aureus, on infected surfaces that you or others may touch.
- Do not share objects. This includes, but is not limited to, personal objects such as bedding, clean towels, razor blades, sports equipment, etc.
- Disinfect all bedding. If skin lesions or amputations are present, all bedding and all sportswear must be washed regularly in hot water with bleach as a disinfectant. As an additional precaution during drying, set the dryer to the highest position.
People with established HA-MRSA are usually quarantined as a precautionary measure until the situation improves. Insulation helps prevent the spread of HA-MRSA infection; the outpatient clinic employees who cared for HA-MRSA patients had fairly strict guidelines and procedures for washing hands. Guests and clinic staff of all types are required to wear protective jackets and gloves to prevent contact with soiled surfaces, and soiled surfaces and bedding of all types are thoroughly disinfected on a regular basis.






