Many readers are interested in the correct subjects of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine. We are pleased to report that our manufacturer has already done research on modern studies on the subject that will fascinate you. We will give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys. Keep repeating to recognize more.
Tell your own doctor or pharmacist if you use other products that cause drowsiness, such as opioid pain or cough medicines (codeine, hydrocodone, etc.), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), other sleeping or confidence drugs (alprazolam, lorazepam, zolpidem, etc.), muscle relaxants ( carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine, etc.) or antihistamines (cetirizine, defenhydramine, etc.).
Butalbital/Acetamide/Caffeine Tablet – Introduction, Side Effects, and Almost Everything Else
Acetaminophen is considered one of the ingredients in this product. Very large doses of acetaminophen can cause severe (possibly fatal) liver damage. Adults are not permitted to take more than 4000 milligrams (4 grams) of acetaminophen per day. People with liver problems and babies should take less acetaminophen. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how many acetaminophen you can safely take.
Do not use other products containing acetaminophen without first asking your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen is in many freely available prescription drugs (such as pain/fever medications and cough medicines). Check the labels of all medications to see if they contain acetaminophen and ask your own pharmacist if you have any doubts.
If you feel well but are taking very large doses of acetaminophen (overdose), seek medical assistance immediately. Signs of overdose include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, sweating, stomach/abdominal pain, severe fatigue, yellow eyes/skin, black urine.
Daily use of alcohol, especially in combination with acetaminophen, can destroy the liver. Be careful with alcohol.
Warnings:
Acetaminophen is considered one of the ingredients in this product. Very large doses of acetaminophen can cause severe (possibly fatal) liver damage. Adults are not permitted to take more than 4000 milligrams (4 grams) of acetaminophen per day. People with liver problems and babies should take less acetaminophen. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how many acetaminophen you can safely take.
Do not use other products containing acetaminophen without first asking your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen is in many freely available prescription drugs (such as pain/fever medications and cough medicines). Check the labels of all medications to see if they contain acetaminophen and ask your own pharmacist if you have any doubts.
If you feel well but are taking very large doses of acetaminophen (overdose), seek medical assistance immediately. Signs of overdose include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, sweating, stomach/abdominal pain, severe fatigue, yellow eyes/skin, black urine.
Daily use of alcohol, especially in combination with acetaminophen, can destroy the liver. Be careful with alcohol.
Usage.
This combination drug is used to treat voltage headaches. Acetaminophen helps relieve headache pain. Caffeine can enhance the effects of acetaminophen; Butalbital is a calming means of reducing anxiety and helping to induce drowsiness and relaxation.
How Butalbital / Acetaminophen / Caffeine Tablets
See also the Warnings section.
As prescribed by a physician, take this medication by mouth with or without food, usually every 4 hours as needed.
If using the water form of this medication, use a special measuring device/spoon to carefully determine dosage. Do not use a household spoon. Because then you will not get the correct dosage.
Dosage is based on your ailment, age, and response to treatment. This drink works better than anything else when used at the first symptoms of headache. If you wait until the headache gets worse, the drink may not activate.
Stopping the medication at a particular moment may result in withdrawal symptoms (nausea/vomiting, mental/mood swings, seizures, etc.). To prevent withdrawal, the physician has the opportunity to slowly decrease the dosage. Withdrawal is more likely if the drug is used for a long time or in large doses. If you are suffering from withdrawal, tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Although it can help almost everyone, this drug can sometimes cause dependence. This risk may be greater if there is impairment in the use of the resource (excessive use or drug/alcohol addiction). Take this medication literally as prescribed to reduce the risk of addiction. Contact your physician or pharmacist for more information.
Tell your doctor if you notice increased use of this medication, that your headaches are getting worse, that the number of headaches is increasing, that the medication is still not working or that you are using this medication more than twice a week. Do not take more than recommended. Your doctor may need to replace your medication or add another medication to prevent headaches.
Side Effects
See also the Warnings section.
Nausea, stomach pain, constipation, dry mouth, tremors (shaking), shortness of breath, excessive urination, lightheadedness, dizziness, drowsiness, or problems sleeping. If one of these effects persists or worsens, tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible.
To reduce the risk of head dizziness and lightheadedness, you should take it slowly if it is prominent or lying down.
Remember that this medication is prescribed because your doctor has determined that the benefit for you is greater than the risk of side effects. Almost everyone using this drug has no serious side effects.
Tell your doctor immediately if you have any serious side effects such as mental/mood changes, fainting, seizures, fast/irregular heartbeat, etc.
Very responsible allergic reactions to this product are rare. Nevertheless, seek medical help if you notice signs of a severe allergic reaction, such as skin rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, hateful breathing.
This is not an absolute list of possible side effects. If you notice any other effects not mentioned above, contact your physician or pharmacist.
In the U.S., call your doctor for medical advice regarding side effects. 1-800-FDA-1088 or you can report side effects to the FDA at www. FDA.Gov/Medwatch.
For medical advice regarding side effects, call your Canadian physician at 1-866-234-2345 to report side effects to Health Canada.
Precautionary Measures
See also the Warnings section.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine if you are allergic to acetaminophen, caffeine or butalbital. or other barbiturates (such as phenobarbital) or xanthine derivatives (such as theophylline); or if you have other allergies. This product contains inactive ingredients that may cause allergic reactions or other problems. Consult your pharmacist for further information.
Before using this medication, you should inform your own physician or pharmacist about the status of your own disease, especially respiratory disorders (such as bronchopneumonia), certain enzyme disorders (porphyria), liver disorders, kidney disorders, your own history of disease or family history of disability in the respiratory tract (e.g., bronchopneumonia), certain enzyme disorders (porphyria), liver disorders, kidney disorders, your own disease history or family history of airway (e.g., bronchopneumonia), your own disease history or family history of disability disability disability disability disability disability disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability Disability
This product may cause dizziness or drowsiness. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you even more dizzy or sleepy. Do not drive, use a car, or do anything that requires caution unless it can be done safely. Be careful with alcoholic beverages. Consult a physician if using marijuana (cannabis).
Liquid product contains alcohol, sugar, and/or aspartame. A conversation is recommended if you have diabetes, alcoholism, liver disease, phenylketonuria (PKU) or another condition that means you need to limit/avoid these products. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about the safe use of this product
Before undergoing surgery or certain medical products (prescription substances, non-prescription fabrics, herbal products), ask your doctor or pharmacist about the harmless use of this product.
Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this product, especially drowsiness and falling asleep. These side effects may increase the risk of falling
During pregnancy, this medication may be used only when clearly needed. Because of the potential for fetal damage, prolonged direction or use at high doses close to the expected delivery date is not recommended. Discuss the risks and benefits with your physician. Babies born to mothers who have used this drug for extended periods of time can ingest withdrawal symptoms such as irritation, abnormal/stopped SOB, nausea, cramps, and diarrhea. If you notice any of these phenomena with your newborn, tell your doctor immediately.
This product turns into breast milk and may have unwanted effects on a nursing baby. Consult your physician before breastfeeding.
Interchange.
See also the Warnings section.
Interactions between drugs can alter the effects of a drug or increase the risk of serious side effects. This document does not include all possible interactions between medications. Keep a list of all products you use (including prescription drugs or including prescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your physician or pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of each medication without encouraging your physician to do so.
Among the products that may well interact with this product are darunavir, oxyvert sodium, isoniazid, ketoconazole, levoketoconazole, lithium, and phenothiazines (such as chlorpromazine).
This product can speed up the removal of other drugs from the body by affecting certain liver enzymes. These affected drugs include doxycycline, estrogens, felodipine, ranafarnine, quinidine, rilpivirine, tamoxifen, theophylline, voriconazole, “blood thinners” (such as warfarin), some beta – spores (such as plus essperolol), pow (Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro loro roll), Paulo loro loro loro l), Paulo loro loro loro roll),
Tell your own doctor or pharmacist if you use other products that cause drowsiness, such as opioid pain or cough medicines (codeine, hydrocodone, etc.), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), other sleeping or confidence drugs (alprazolam, lorazepam, zolpidem, etc.), muscle relaxants ( carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine, etc.) or antihistamines (cetirizine, defenhydramine, etc.).
Check the labels of all medications (e.g., allergy and cough medicines). This is because they can contain caffeine or ingredients that cause drowsiness. Also check that certain drinks (coffee, colas, teas, energy drinks, etc.) contain caffeine. Ask your pharmacist about the safe use of these products.
This medication may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraception such as pills, plasters, rings, etc. Can produce pregnancy. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you want to use an extra reliable contraceptive method with this medicine. Also tell your doctor if you are suffering from new spotting or breakthrough bleeding. This is because this can be a symptom of contraception not working.
This drug may confound certain medical/clinical tests, which could result in incorrect test results. Make sure that the lab staff and all physicians understand that you are using this product.
Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine
Fixed Title: Acetaminophen, Butalbital and Caffeine [A-SEET-A-HOH-FEN, BUE-TAL-BI-VI-VI-VI-A]: ESGIC, FIICET, ZEBUTAL, ESGIC-PLUS, ARCET, ALCET, all 37 brands Isocet, Pharmagagesic, Anoquan, 2-Dynamic, Tenake, Margesic, Anolor 300, Femcet, Geone, Tencet, Triad, Fiorap, Dopan, Dolmar, Ezol, Ide-Cet, G-1, Meditative Tative, Mygracet, Pacaps, Alages, Alages , Americet, Non BAC, Dolgic LQ, Dolgic Plus, Orbivan, Capace, Vanatol LQ, Vanatol S, Vtol LQ, Formulation: oral capsule (300 mg-40 mg; 325 mg 40 mg); oral liquid (325 mg-50 mg-40 mg/15 ml); oral tablets (325 mg-50 mg-40 mg) drug class: anesthetic combinations
From the point of view of the physician evaluated by the drug. com on January 21, 2022.
What are acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine?
Acetaminophen is considered an anesthetic and fever reducer.
Butalbital belongs to a group of drugs called barbiturates. It relieves muscle deposits associated with tension headaches.
Caffeine is considered a catalyst for the central nervous system. It relieves vascular muscle vessels and improves blood flow.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine are combination medications used to treat voltage headaches caused by muscle relaxation.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine can still be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Warning.
Do not use this medication if you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. Unsafe drug interactions may occur; MAO inhibitors include isocarboxide, linzolid, methylene blue injection, phenoldine, and troilcypromine.
Do not take more Sego medications than recommended. Acetaminophen overdose can destroy the liver or cause death. Call your doctor immediately if you suffer from nausea, upper abdomen, itching, loss of appetite, black urine, distorted stools, yellow und (turning yellow from the skin or eyes).
Rarely, acetaminophen can cause skin reactions. Yes, stop taking acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine and call your own doctor immediately if you suffer from redness of the skin or rash.
Before taking this medication.
Do not use this medication if you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. Unsafe interactions between medications may occur; MAO inhibitors include isocarboxide, linear, phenoldine, rasagiline, selegiline, and troilcypromine.
If you have allergies, porphyria, or have recently used alcohol, tranquilizers, or other opioids, you should not use acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine.
Tell your doctor if you ever
- Liver disease, cirrhosis, alcohol or drug abuse, or if you drink more than 3 alcoholic beverages per day
- Kidney disease; or
- Stomach ulcers or bleeding; or
- History of drug-induced skin conditions; or
- Mental disorder or suicidal thoughts.
It is not known if this drink is harmful to the fetus. If butalbital is used during pregnancy, the baby may become dependent on the product. This can lead to life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after birth. Babies born on conventional medications may require treatment for several months. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or want to become pregnant.
This medication turns into breast milk and can be harmful to your baby. Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding your baby.
Not approved for use by people under 12 years of age.
How do I stop taking acetaminophen, butalital, or caffeine?
Follow all instructions on your own prescription label. Take the recommended dosage of the medication. An overdose can destroy your liver or cause death. Tell your own doctor if the medication no longer seems to be working and should illuminate and lighten your pain.
Butalivital can become habit-forming. Do not use acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine with anyone else. Keep the medication in a room where others cannot reach it. It is against the law to sell or give away this medication.
Keep at room temperature, away from moisture and heat.
Keep track of the number of each fresh bottle used.Butalbital is a drug for abuse and you are obligated to the nobility whether or not someone is using your drug incorrectly and without prescription.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Since this medication is used when needed, you may not follow the dosing schedule. If you do follow the schedule, use the missed dose as soon as you think of it. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for the correct planned dose. Do not use additional medications to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Find appropriate medical help or call anti-giflijn at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of acetaminophen, butalivital, or caffeine can be fatal.
The first symptoms of acetaminophen overdose are lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, sweating, loss or helplessness. Later symptoms are pain in the upper abdomen, black urine, yellow skin and whitish eyes.
Symptoms of overdose are still insomnia, agitation, tremors, diarrhea, superficial breathing, irregular heartbeat, convulsions (seizures) or fainting.
What should I ignore when using acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine?
These medications can cause side effects that may make it worse for you to think or react. Use caution when you drive or do anything that requires you to be awake and alert.
Avoid the use of alcohol. This increases the risk of liver damage when using acetaminophen.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist before using it for another cold, allergy, pain, or sleep aid. Acetaminophen (sometimes abbreviated as APAP) is a concomitant medication in many When certain products are ingested, very large amounts of acetaminophen may be available and can lead to a fatal overdose. Check the label to see if the medication contains acetaminophen or APAP.
When using this medication, be wary of taking food pills, caffeine tablets, or other stimulants (such as ADHD medications) without medical advice.
Side Effects of Acetaminophen, Butalivital, and Caffeine
If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek emergency medical assistance: hive; difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Rarely, acetaminophen can cause serious skin reactions that can be fatal. This can occur even if you have taken acetaminophen in the past and had little or no reaction. Yes, if you stop taking acetaminophen, butalivital, or caffeine and get redness from the skin or a rash that causes calluses or pargers to stretch out, call your own doctor immediately. If there is such a response pattern, you are not obligated to take the drug with acetaminophen.
This drug has the ability to cause nonsense side effects. Stop using this medication and call your own physician immediately if you are suffering from
- Confusion, accidental;.
- Shortness of breath;.
- A light sensation in your head, as if you could lose consciousness . Or.
- Nausea; pain in the abdomen, itching, loss of appetite; black urine; relief of the skull; yellow und (turning yellow from the skin or eyes).
Side effects of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine are common.
- Drowsiness; Dizziness;.
- Sensation of dizziness;.
- Nausea; Nausea; Abdominal pain; or
- Dull feeling; or
- Shortness of breath.
This is not an absolute list of side effects. Other side effects may occur. Ask your doctor about side effects; you can report side effects to the FDA by calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
Information on the administration of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine
Usual dosage for mature headache:
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 300 mg/Caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules orally every 4 hours as needed, but no more than 6 capsules per day.
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 325 mg/Caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 rounds orally every 4 hours as needed, but not more than 6 capsules or tablets per day.
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 325 mg/Caffeine 15 ml per 15 ml of water, oral use: 15 to 30 ml every 4 hours as needed, but not more than 90 ml per day.
Remarks: – Prolonged use of this product is not recommended due to increased physiological dependence. -Safety and effectiveness of the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches with the help of this product is unknown.
Indications: For relief from the symptom complex of tension headache (or muscle contractions).
Usual children’s dosage for headache:
12 years and older:
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 300 mg/Caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules orally every 4 hours as needed, but no more than 6 capsules per day.
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 325 mg/Caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 rounds orally every 4 hours as needed, but not more than 6 capsules or tablets per day.
Butalbital 50 mg/Acetaminofen 325 mg/Caffeine 15 ml per 15 ml of water, oral use: 15 to 30 ml every 4 hours as needed, but not more than 90 ml per day.
Remarks: – Prolonged use of this product is not recommended due to increased physiological dependence. -Safety and effectiveness of the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches with the help of this product is unknown.
Indications: For relief from the symptom complex of tension headache (or muscle contractions).
Which other substances affect acetaminophen, butalbital or caffeine?
Taking this medication with other products that cause drowsiness or breathing distortion can lead to serious or life-threatening side effects. Before taking acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine with sleeping pills, opioid anesthetics, muscle relaxants, or drugs for anxiety, depression, or epileptic seizures.
Other substances are more likely to affect acetaminophen, butalital, and caffeine, including prescription and freely available medications, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform your doctor about all other medications you use.
Where can I find support information?
Remember to keep this and all other medications out of the reach of children. Do not share your medicine with other medicines.
More about Acetaminophen / Butalbital / Caffeine
- Check for interactions
- Prices and Coupons
- Reviews (244)
- Narcotic Pictures
- Side Effects
- Dosing Information
- Advice for Patients
- Pregnancy
- Drug Classes: Anesthesia Combinations
- and español
Patient Source
- Advanced Reading
- caffeine capsules and pills and caffeine pills and caffeine pills and caffeine pills and caffeine pills
- butalbital, acetaminofen and caffeine solutions
Other Brands
Professional Sources
Related Treatment Authorities
For more information
Always consult your care provider to ensure that the information on this page is used for your own incident.
Copyright 1996-2023 Cerner Multum, Inc. version: 8. 01.
Prescribing Information on Butalbital, Acetaminofen and Caffeine
Medical Testing with Drugs. com. last updated January 1, 2023.
On this page.
- Package Warning
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Indications and Uses
- Contraindications
- Warning.
- Precautionary Measures
- Information on Patient Guidance
- Medication Interactions
- Adverse Reactions
- Abuse and Dependence
- Overdose
- Medication and Administration
- Delivery/Storage and Handling
Liver Poisoning
Acetaminophen has been associated with variants of acute liver insufficiency, sometimes resulting in liver transplantation and death. The majority of cases of liver injury are associated with the administration of acetaminophen at doses greater than 4000 milligrams per day, often involving one or more products containing acetaminophen.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Description
Butalbital, Acetaminofen, Caffeine Pills, USP is supplied in tablet form for oral administration.
Each tablet has the appropriate functional ingredients.
Butalbital, USP 50 mg Acetaminofen, USP 325 mg Caffeine, USP 40 mg
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, crosvidone, crosmellose sodium, corn starch, stearic acid, facility oxide, colloidal silicon, magnesium stearate, FD & amp; C Blue #1.
Butalbital (5-allyl-5 isobutyl barbiturates) is a short to moderately effective barbiturate. Contains the correct structural formula.
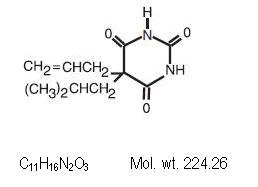
Contains the correct structural formula
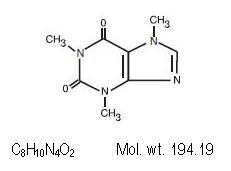
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is considered a central nervous system catalyst. Contains the proper structural formula.
Related/similar drugs
Butalbital, Acetaminofen and Caffeine-Clinical Pharmacology
This combination drug is specialized for curing tension headaches.
It consists of a fixed composition of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine. The role of each component in relieving the overall symptoms common as tension headache has not been fully investigated.
Pharmacokinetics
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Butalbital is supposed to be completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and partitioned into most body tissues. Barbiturates generally end up in breast milk and may only pass through the barrier in that location. They commit themselves to various plasma and tissue proteins, and binding increases especially with lipid solubility.
Butalbital is excreted mainly by the kidneys (59-88% of the dose) in unchanged form or in the form of metabolites. The half-life of plasma elimination is less than 35 hours. Urinary excretion products include the original drug (about 3.6% of dose), 5-isobutyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)barbituric acid (about 24% of dose), 5-alyl-5(3-hydroxy-) (2)-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid (about 4.8% of the dose), urea (about 14% of the dose), which is hydrolyzed by the barbituric acid ring, and products that release non-deposited material. Of the material excreted in urine, 32% is considered conjugated.
The binding of butalbital to plasma proteins in vitro forms 45% in a concentration spectrum of 0, 5-20 µg/ml. This corresponds to the plasma protein binding spectrum (20-45%) observed with other barbiturates such as phenobarbital, pentobarbital and secobarbital sodium. The relationship between plasma and blood concentrations is nearly identical to unity, indicating no preferential distribution of butalital in plasma or blood cells.
For more information on toxicity, see the Provisional Dosing section.
Acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and spread to most tissues of the body. The duration of plasma elimination half-life varies from 1.25 to 3 hours, but may increase in cases of liver damage and overdose. Acetaminophen excretion occurs primarily by hepatic metabolism (binding) and further excretion of metabolites by the kidneys. Approximately 85% of orally administered doses are excreted in the urine within 24 hours of administration. Usually in the form of gluconide jugat, with small amounts of other conjugated and unaltered products.
For more information on toxicity, see the Provisional Dosing section.
Like most xanthines, caffeine is quickly absorbed and metabolized in all tissues and body fluids, including CZ, fetal tissue, and breast milk.
Caffeine is removed by metabolism and excreted in the urine. The half-life of plasma is less than 3 hours. Biotransformation in the liver prior to excretion results in approximately equal amounts of 1-methylxanthine and 1-methyluric acid. Of the 70% of the dose in the urine, only 3% is permanent drug.
For more information on toxicity, see the Provisional Dosing section.
Indications and Dosing of Butalbital, Acetaminofen and Caffeine
Butalbital, Acetaminofen and Caffeine Pills, USP is indicated for the symptomatic relief of voltage headaches (or muscle contractions).
Data supporting the efficacy and protection of this combination product in the treatment of numerous periodic headaches are not available; caution should be exercised as Butalbital is addictive and possibly considered inappropriate.
Contraindications
This product is contraindicated under the correct criteria.
– Hypersensitivity or intolerance to the components of this product – Patients with porphyria.
Warning.
Liver Poisoning
Acetaminophen is associated with a variant of acute liver injury, which can lead to liver transplantation and death. Most cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses exceeding 4000 milligrams per day, often with one or more products containing acetaminophen. Excessive use of acetaminophen can cause intentional self-inflicted injury or unintentional, as patients attempt to relieve more pain or unintentionally ingest other acetaminophen-containing products.
The risk of acute liver deficiency is increased in persons with severe liver disease and in those who use alcohol while using acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to pay attention to the acetaminophen or APAP on the package label and not to use more than one product with acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical assistance immediately after using more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well.
Severe skin reactions
Rarely, acetaminophen can cause severe skin reactions such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJ), and toxic epidermal necrosis (10). Patients must be informed of the symptoms of non-severe reactions and product introduction should be stopped at the first occurrence of a skin rash or the first occurrence of other symptoms of hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis
A post-marketing notification of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis was associated with the introduction of acetaminophen. Clinical symptoms were edema of the face, mouth and larynx, dyspnea, ur measles, skin rash, pruritus, and nausea. There were exceptional reports of non-aggressive anaphylaxis requiring immediate medical assistance. Instruct patient to stop butalbital, acetaminofen, and caffeine pillars immediately and to seek medical assistance immediately if they experience these symptoms. write butalbital, acetaminofen, and caffeine pills, and to avoid taking acetaminophen if they are allergic to acetaminophen. Do not give USP to patients who are allergic to acetaminophen.
Butalbital is considered an attachment builder and can be abused. Therefore, long-term use of this product is not recommended.
Precautionary Measures
In general
Butalbital, Acetaminofen, and USP for Caffeine Tablets should be administered with caution to patients at increased risk, including elderly or weakened patients, patients with severe kidney or liver dysfunction, or acute animals.
Information for Patients/Guardians,
This product may affect the intellectual and/or physiological abilities necessary to perform potentially unsafe tasks, such as operating a motor vehicle or operating machinery. These tasks should be ignored while using this product.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants can cause addictive CNS depression when taking this combination product and should be avoided.
Butalbital is addictive. Patients should take the product only as long as it is prescribed, not in the doses specified.
For use in geriatric patients, see “Precautionary Measures/ Geriatric” in this package leaflet. Precautionary Measures / Geriatric Implementation.
– Do not take butalbital, acetaminophen, or caffeine pills if you are allergic to any of the respective ingredients. – If you have any symptoms of allergy, such as skin rash or difficulty breathing, stop taking butalbital, acetaminophen, caffeine pills, USP and contact your doctor immediately. If you are taking more than the correct dose, call your own physician.
Clinical Examination
In patients with liver or kidney disease, the effects of treatment are kept under control using serial liver and/or kidney studies.
Medication Interactions
The effects of CNS Butalivital can be enhanced by monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOs).
Butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine can enhance the effects of other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, joint anesthetics, calming agents such as chlordiazepoxide, or other CNS depressants that cause CNS depression.
Interactions Between Drugs and Laboratory Tests
Acetaminophen can cause false positive test results for 5-hydroxindoleic acid in urine.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, and fertility issues
No adequate animal studies have been conducted to determine whether acetaminophen or butalivital carcinogenesis, mutagenicity, or fertility loss is caused.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category c
There are no animal reproduction studies with this combination product. It is not yet clear whether butalital, acetaminophen, or caffeine can cause fetal damage or may affect birth when administered to a pregnant woman. This product may only be given to pregnant women when clearly needed.
Non-psychotic effects
Withdrawal symptoms were reported in infants two days after their mothers received a product containing butalbital during the last two months of pregnancy.Butalbital was found in the baby’s serum. The baby received phenobarbital 5 mg/kg. This was phased out without any signs of subsequent attacks or other withdrawals.
Breastfeeding mothers.
Caffeine, barbiturates, and acetaminophen are excreted in small amounts in breast milk, but the implications of their effects on a nursing baby are unknown.Butalbital, acetaminofen, and caffeine have the potential for serious side effects in children, so mothers consider the products important, reasonable to determine if breastfeeding should be stopped or if the products should be discontinued.
Pediatrics
Safety and efficacy have not been determined for pediatric patients under 12 years of age.
Geriatric
In the clinical studies of Butalbital, Acetaminofen, and Caffeine Pills, the USP does not include the required number of described subjects over 65 years of age to determine if they respond differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical skills did not show differences in response between older and younger patients. In general, dosages should be carefully selected for older patients, who typically start at the bottom of the dosing spectrum, because of the higher incidence of decreased liver, kidney, or heart function, concurrent disease, or other pharmaceutical therapies.
Butalbital is known to be quite differentiated by the kidneys, and the risk of toxic reactions to this product may be higher in patients with reduced renal function. Elderly patients are at higher risk of renal function decline, so it is prudent to be careful with dosage and may have a healthier renal prognosis.
Side Effects
Frequently observed.
The most reported side effects are drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, respiratory, drowsiness, nausea, abdominal pain, and feeling intoxicated.
Rarely.
All unwanted incidents represented below are labeled as rarely observed.
Central nervous system: headache, unsteady, tingling, excitement, fainting, fatigue, slow eyelids, supreme energy, hot hours, numbness, slowness, coincidence. Mental confusion, anxiety, or depression may occur as a result of intolerance, especially in old or weakened patients, or as a result of butalbital overdose.
Autonomic nervous system: dry mouth, hypertension.
Tour lobe: dysphagia, heartburn, flatulence, constipation.
Musculoskeletal firm: leg pain, muscle fatigue.
Miscellaneous: Pritas, fever, ear ringing, stuffy nose, ear rattling, euphoria, allergic reactions.
Several cases of skin reactions have been reported, including toxic epidermal necrosis and erythema multiforme.
The following side effects can be considered possible effects of this product component The effects at possibly the highest doses are listed in the overdose section.
Acetaminophen: allergic reactions, skin rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Caffeine: cardiac irritation, irritability, tremors, involuntary, nephrotoxicity, hyperglycemia.
Abuse and Dependence
Drug abuse and dependence
BUTALBITAL
Barbiturates can become habit-forming. Tolerance, mental and physical bondage can occur, especially after prolonged use of large doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for barbiturate addicts is usually about 1500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates increases, the number needed to maintain the same value of intoxication. However, with fatal doses tolerance increases twofold. When this occurs, the margin between the intoxication dose and the fatal dose becomes smaller. Prior to death, if alcohol is still flowing, the barbiturate dose is much lower. The most important withdrawal symptoms (seizures and delirium) are in the direction of 16 hours after stopping abruptly on these substances, and have the opportunity to run as long as 5 days. The intensity of withdrawal symptoms decreases gradually after about 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence is based on careful and gradual withdrawal of the product. Barbiturate-dependent patients have the opportunity to reduce any chance of withdrawal by introducing various finishing schedules; one method consists of starting treatment at a constant dose level for the patient and gradually decreasing the daily dose tolerated by the patient.
Overdose
Following an acute overdose of butalibital, acetaminophen, or caffeine, toxicity may be the result of barbiturates or acetaminophen. Because of the relatively small number associated with this, caffeine-induced toxicity is the least likely.
Drawings and Symptoms
Barbiturate toxicity includes drowsiness, confusion, com sleep. respiratory depression; hypotension; and blood loss shock.
Overdose with acetaminophen: dose-dependent, potentially fatal liver necrosis is considered a slightly irritating side effect. Necrosis of the renal tubules, hypoglycemia com sleep, and coagulopathy still have every opportunity to run. Initial symptoms after a possible hepatotoxic overdose are nausea, vomiting, paralysis, and malaise. Clinical and laboratory delivery toxicity certificates are available only 48-72 hours after administration. In adults, liver toxicity is sometimes described with a rapid overdose of less than 10 grams or killed with less than 15 grams.
Acute intestinal infection with caffeine can cause insomnia, agitation, tremors and absurdity, tachycardia and subfluctuations.
CARE
A single off or repeated overdose with this combination product may result in a fatal overdose of the poly drug and consultation of a local antigif center is recommended.
Treatment required includes cardiopulmonary support and means to reduce product absorption. There are indications for the use of air, intravenous water, boosting agents, and other supportive measures. Consider the possibility of support or controlled ventilation.
Gastric decontamination with activated charcoal should be performed immediately before N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to reduce systemic absorption if known or if acetaminophenrut is expected to be performed within hours of admission. Serum acetaminophen levels should be determined immediately if patient contact occurs more than 4 hours after ingestion to assess the potential risk of hepatotoxicity. Acetaminophen values determined within 4 hours of ingestion can be misleading. For best results, NAC should be administered as soon as possible in the presence of suspected impending liver injury. If oral administration is not possible, NAC can be administered intravenously.
When serious intoxication occurs, aggressive supportive care is critical. Because liver damage is dose-dependent and occurs in the early stages of poisoning, steps to limit constant absorption of the product should be taken without delay.
Butalbital, Acetaminofen and Caffeine: Dosage and Administration
1 or 2 tablets every 4 hours as needed. Total daily dosage may not exceed 6 tablets.
Prolonged and repeated use of this product is not recommended due to the potential for physiologic dependence.
How Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine are administered
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Tablets, USP contains 50 mg of butalbital, 325 mg of acetaminophen, and 40 mg of caffeine.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Tablets, USP, 50 mg/325 mg/40 mg are round with no blue spots with “1695” on one side and “LCI” on the other and are supplied in the appropriate package.
10 tablets per package in bags, NDC 55154-3356-0.
Saves 20-25°C (68-77°F) [see NDC 55154-3356-0. Controlled Room Temperature USP.”
Pharmacopoeia to be issued in impenetrable packages as prescribed in the U.S., Children – Safe Lid (if applicable).
Distributed by Lannett Company, Inc. Philadelphia, PA 19136.
Dublin, Ohio 43017.
Made in the U.S.A.
Packaging/ Labeling Reflection Panel
butalbital, acetaminofen and caffein pills, usp
50 mg/ 325 mg/ 40 mg

| Product Information | |||
| Type | Fabric Etiquette for human repetition | Product code (source) | ndc: 55154-3356 (ndc: 0904-6938) |
| Management | Oral | Management of Drug Administration Schedules | |
| Active Component | ||
| Name Component | Based on strength | Butalbital (butalbital) |
| BUTALBITAL | butalbital | 50 mg |
| Acetaminophen (acetaminophen) | acetaminophen | 325 mg |
| Caffeine (caffeine) | Coffee – decay | 40 mg |
| Inactive Ingredients | |
| Name Component | Butalbital (butalbital) |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | |
| Crospovidone | |
| Sodium croscormellose | |
| Corn starch | |
| Coagulant acid | |
| Silicon dioxide | |
| Magnesium stearate | |
| fd& amp; C Blue No. 1 | |
| Product Properties | |||
| Color | Blue (light blue, speckled) | Account | No score |
| Shape | crotch | Size | 11 mm |
| Taste | Fingerprint Code | LCI; 1695 | |
| Includes | |||
| Package | |||
| # | Product Code | Packaging Description | |
| 1 | NDC: 55154-3356-0 | 10 blister packages in 1 bag | |
| 1 | Blister packaging 1 pill | ||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Order number or quoted monograph | Marketing Start Date | Set the end date |
| and a | ANDA200243 | 13. 09. 2012 | |
| Label – Cardinal Health 107, LLC (118546603) |
Cardinal Health 107, LLC
More about Acetaminophen / Butalbital / Caffeine
- Check for interactions
- Prices and Coupons
- Reviews (244)
- Narcotic Pictures
- Side Effects
- Dosing Information
- Advice for Patients
- Pregnancy
- Drug Classes: Anesthesia Combinations
- and español
Patient Source
Professional Sources
- Information on Prescriptions
- Butalbital, acetaminophen and caffeine solution (FDA)






