Many readers are interested in the right subject: blood clots. Our makers are pleased to report that they have already done modern research studies on your fascinating subject. We can give you a wide range of answers based on the most recent medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys. Find out more.
Blood clots can cause serious health problems and may be a cause for concern. When people know the anatomy and function of blood vessels and the disorders and phenomena associated with blood clots, they can take precautions to assure their well being.
When blood clots occur in the veins, this is commonly known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) at its deepest. These clots are often found in the legs and can cause swelling, pain, and problems with movement and standing. It is important to note, however, that not all clots are considered DVT, as they can occur in other parts of the body as well.
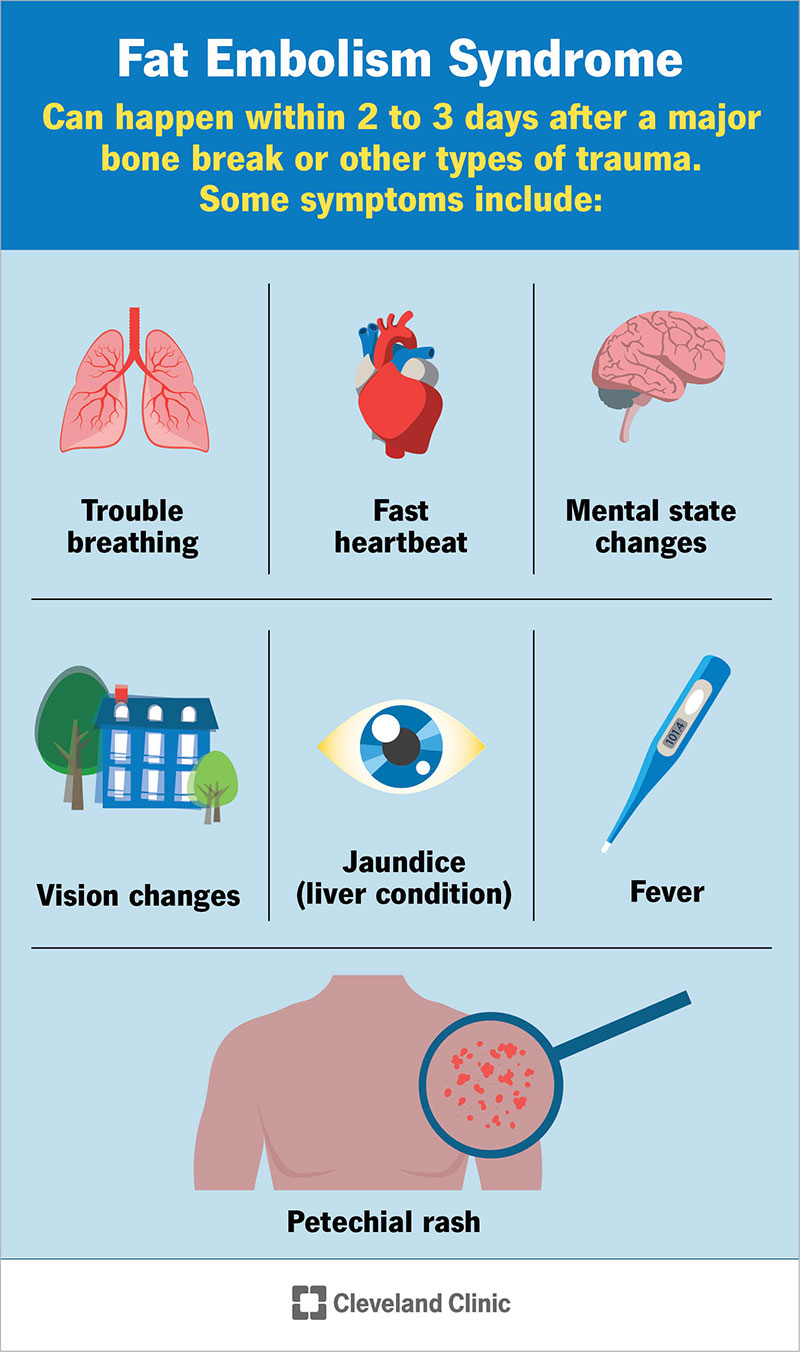
If a clot travels to a critical area, this can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition known as pulmonary embolism. Signs of pulmonary embolism include shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, and coughing up blood. When these symptoms occur, direct medical assistance is critical.
Some clots are relatively flexible and self-reliant, while others can be more serious. Some people are at increased risk for clots, such as those with a family history of coagulation disorders or disorders such as diverticulitis or V Leiden’s moment. In addition, prolonged immobility, for example during prolonged air travel, may increase the risk of blood clots.
To prevent blood clots, it is important to remain physically focused, especially if working for long periods of time. Wearing compression garments and hydration increases the likelihood of maintaining healthy blood flow. If you suspect you have a blood clot, it is important to consult your physician.
To prove the diagnosis and get the right treatment.
In this informative visual guide, we will look at the external image and signs of blood clots and all the various inexpensive ways to treat them. By learning how to recognize and eliminate blood clots, people can protect their health and well being.
What exactly is a blood clot?
A blood clot is a sharp formation that occurs in the body during the blood clotting process and functions to maintain blood flow and stop bleeding. Blood clots have every opportunity to originate in different parts of the body, such as arteries, veins, or the heart. Blood clotting is a normal process that helps the body heal amputations and contusions, but problems can occur when clots form in spaces where clotting does not exist or when clots form when not properly resolved.
Clots can occur for a variety of reasons, including reduced blood flow, arterial injury, and blood diseases. It is estimated that more than 900,000 people in the United States alone have to deal with blood clots each year, and the risk increases with age.
When blood clots form in the arms, legs, or other limbs, this is called thrombosis of the veins beneath (DVT). This can lead to symptoms such as swelling, pain, and discoloration in the affected area; if the DVT remains untreated, it can lead to more serious conditions, including pulmonary embolism.
Embolization occurs when a blood clot comes from its original location and travels to another part of the body, such as the non-energetic or brain. If something is not done about this in time, this can lead to life-threatening complications. Signs of pulmonary embolism include a mild cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and more frequent heartbeats. Additionally, signs of cerebral embolism can result in visual disturbances, headaches, and speech problems.
Do not avoid symptoms of blood clots. It is also important to seek medical assistance if you suspect you have them. Certain points, such as a history of coagulopathy or a condition called Leiden’s v-oment, may increase the likelihood of clots. Additionally, certain lifestyle habits such as smoking and lack of physiologic potency may also contribute to thrombus.
When it comes to blood clots, a prompt and clear diagnosis is critical. Medical staff can use a variety of methods, including scans and blood tests, to take a complete picture of the clot and qualify an appropriate treatment project. Treatment options are drug therapy to resolve the clot or surgery to remove it.
Thus, a blood clot is a formation that can occur for a variety of reasons, including reduced blood flow, damage to blood vessels, and certain health conditions. They are more likely to occur in different parts of the body and are more likely to cause a variety of symptoms. If you suspect a blood clot, it is important to seek immediate medical attention to avoid the possibility of serious deterioration.
Recognizing Formation
When a blood clot forms in a vein, it can cause stasis and block blood flow. This is known as a venous thrombus. It often occurs in the legs and lower extremities, where blood flow is slow. They can also occur in the arms, pelvis, or other parts of the body. If the clot detaches and heals without serious consequences, it can cause a pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening.
There are a number of specific health conditions that can increase the risk of clot formation, including pulmonary embolism (DVT) and PE (pulmonary embolism). Other pointers include prolonged immobility, such as during airplane travel or bed rest, pregnancy, obesity, smoking, and certain genetic conditions such as Leiden’s V-moment. It is important not to avoid the signs and risk points associated with blood clots.
How blood clots form
When blood vessels are damaged, the body’s clotting mechanism is activated to stop the bleeding. Platelets and proteins in the blood form a sticky plug at the site of injury, sealing the vessel and promoting healing. This is called platelet aggregation.
In some cases, the coagulation apparatus may malfunction and a clot may form in the blood vessel without causing damage. This is known as a thrombus. They can occur in veins and arteries and can cause a variety of health problems. For example, a clot in an artery can cause a heart attack or myocardial infarction, while a clot in a vein can cause deep vein thrombosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clots
- For example, it is important to know what the signs and symptoms of a blood clot are because they can all vary depending on the location of the clot. Joint signs may include
- Swelling and pain in the affected area
- Heat and redness in the area of the clot
- Obviously large or bulging veins
- Dyspnea or chest pain if the clot travels to the lungs
- Bleeding or coughing that does not stop
- Agitation or weakness
Nausea, or nausea if the thrombus is in the mesenteric artery
If you feel one of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical assistance immediately. Do not make a diagnosis and do not touch yourself. Only a physician can make the correct diagnosis and treat the clot.
Aggravation and Risk
There are many complications and risks owed to the nobility when it comes to blood clots. If not intervened immediately, a blood clot has the chance to have nonsense consequences on your well-being.
- Complications:
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): DVT occurs when a blood clot appears deep in a vein in the leg or pelvis. It can cause pain, swelling, redness, and heat in the affected area. If untreated, the clot can break loose and travel to a non-pulmonary vein, leading to a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): PE occurs when a blood clot travels from a leg or pelvic vein into a non-pulmonary vein. Symptoms are dyspnea, sharp chest pain, fast heartbeat, and blood cough.PE is a medical emergency and requires the immediate attention of medical staff.
Post Dental Syndrome: This syndrome can occur after DVT and can worsen over time, including leg pain, swelling, and problems walking. If these symptoms are experienced, it is important to find treatment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/blood-clot-symptoms-5b2a730c04d1cf0036128d59.png)
Risks:
- There are all kinds of risk points that have the opportunity at every opportunity to increase the chances of getting a blood clot. These include
- Having a blood clotting situation
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- Sitting or not moving for long periods of time
- Has certain diseases such as cancer, kidney disease, diverticulitis
- Has an operation or trauma
- Use of hormonal contraception or hormone replacement therapy
Has a family situation of blood clotting disorder such as Leiden Moment v
Prevention:
- To reduce the risk of getting blood clots, doctors often have the opportunity to advise
- Keep focused and exercise regularly
- Do not sit or stand for long periods of time
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Wear support stockings when traveling or for many years
- Stay hydrated
Follow a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables and inseparable grains
If you are at high risk for blood clots, your doctor may prescribe you medications or other treatments to prevent their formation
In general, it is important to be aware of your personal health and the complications, risks, and prevention of blood clots. If you feel one of the signs or have questions, it is important to discuss them with your care provider.
What do blood clots look like?
Blood clots, also known as thrombus, can look different depending on where they originate and where they are located. Common characteristics of a blood clot include
Size and shape
Blood clots can vary widely in size from small to large. They may be round or elongated, and their shape may vary depending on the blood vessel in which they originate. In arteries, clots tend to be more irregular in shape, while veins tend to be more elongated.
Color
Blood clots can have different colors, depending on their age and composition. Strong blood is often reddish or brooding red, while older clots may appear yellowish or brownish. The color change occurs when the clot fails and is reabsorbed by the hull.
Texture.
Clot texture can range from hard to gel-like. Strong clots are usually fleshy and appear jelly-like, while strong clots are hard and rigid.
Location.
- Blood clots may be created in many different locations in the body. Some common places where clots are likely to form:
- Deep veins in the legs (known as deepest vein thrombosis or DVT)
- Arteries
- Heart (known as pulmonary embolism)
- Lungs (known as pulmonary embolism)
Brain (leading to stroke)
Symptoms
- Symptoms of a blood clot may vary by location and volume. Some common symptoms include
- Pain or sensitivity in the affected area
- Swelling, warmth or redness in the leg or arm
- Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain or cough (for pulmonary embolism)
Headache on one side of the body, visual configuration, or impotence (in stroke)
Treatment and Prevention
If a blood clot is suspected, find medical help. Effective healing and prevention strategies are available, including medications to resolve clots and prevent further clot formation. In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove or bypass the clot.
To prevent blood clots, it is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes heavy exercise, a balanced diet, and avoidance of prolonged immobility. If you have a specific disease or disorder that increases your risk of blood clots, your physician can recommend specific preventive measures.
Remember that blood clots can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to seek medical assistance immediately if you feel any signs that could indicate a blood clot.
- Common signs of blood clots
- Painful cramps: one combination of symptoms of a blood clot is painful cramps, usually in the lower legs or calves. The pain may be felt as muscle tightness, but is characterized by greater difficulty.
- Swelling: Blood often causes swelling in the affected area. This swelling may be accompanied by redness and warmth of the skin.
- Skin color change: the skin over a blood clot may change color and bleach or blue due to decreased blood flow.
- Warm feeling: if you notice a warm feeling on the skin, especially around the possible clot area, this can be a symptom to seek medical help.
- Chest Pain or Dyspnea: A non-emotional blood clot, known as a pulmonary embolism, can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing. This is a potentially life-threatening deterioration that requires immediate medical assistance.
- Headache, Dizziness, or Fainting: Blood clots that have gone to the brain can cause symptoms such as headache, dizziness, or fainting. These neurological symptoms should not be ignored and should be evaluated as soon as possible by a health professional.
- Unexplained cough or blood cough: In some cases, blood clots form in the veins of the legs and have a chance to travel to non-pulmonary veins, leading to a condition known as pulmonary thrombosis. This can lead to a blood cough or inexplicable cough or obstruction.
Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting: blood clots in the veins of the abdomen, as caused by diverticulitis or cancer, can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience these symptoms along with other symptoms of blood clots, it is important to seek medical assistance.
Paying attention to these common signs of blood clots can help you detect them quickly and prevent further complications. If you or one of your loved ones notices any of these signs, don’t he to seek medical help. Timely treatment can make a big difference in preventing more serious health problems.
Remember that not all blood clots have definite symptoms or signs. Therefore, if you are concerned about your health or suspect that you are at risk for blood clots, consult your physician. He or she can give you advice and help you need for your well
blook Blood Clot-Related Disorders and Disorders
- There are a number of disorders and impairments that are very often associated with blood clots. Recognizing these disorders and impairments and detecting them early and then treating them can be very helpful. Some of the common conditions and disorders associated with blood clots are
- Superior Venous Thrombosis (SVT): SVT is a condition in which a blood clot forms in an upper vein in the leg or pelvis. Characterized by symptoms such as swelling, pain, and problems walking, DVT can be a serious complication and requires urgent immediate medical attention.
- Pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot advances into non-pulmonary areas and blocks blood flow. Signs of pulmonary embolism are chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. This is not a life saving condition and requires immediate medical assistance.
- Stroke. A stroke is caused by a blood clot that closes off the blood supply to the brain. This can lead to many symptoms, including sudden numbness or helplessness on one side of the body, problems with speech and language recognition, and severe headaches. In the case of a heart attack, immediate medical assistance is critical.
- Peripheral vascular disease. Peripheral vascular disease occurs when a blood clot forms in an artery that provides blood to a leg, arm, or other limb. Signs are pain, numbness, and difficulty walking. Cure options for peripheral vascular disease depend on the severity of the condition.
- Venous thromboembolism. Venous thromboembolism is a syndrome that includes both deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It is a potentially life-threatening and critical condition if not treated promptly.
- Wilbrand’s Field Disease: Wilbrand’s Field Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the ability of blood to clot. This can lead to severe bleeding and bruising. Treatment options for Willebrand’s disease include the use of medications and avoidance of certain behaviors that may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Mesenteric ischemia: mesenteric ischemia occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow to the intestinal tract. Signs include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Immediate medical assistance is important to prevent further complications.
It’s important to note that blood clots can be associated with other conditions and disorders in addition to the ones mentioned above. If you notice any symptoms that may indicate a blood clot or if you have a history of blood clots, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications and ensure a better outcome.