Many readers are interested in the right subject: basal cell carcinoma of the nose: species, identification, and cure. Our makers are pleased to report that they have already studied contemporary research on this fascinating subject. We will give you a wide range of answers based on information from the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample surveys. Keep reciting to recognize more.
When it happens to be your nose that is being noticed, basal cell carcinoma It may look like an elegant yellowish spot, a reddish spot, a fantastic ridge, or an oath you don’t want to heal.
Basal Carcinoma Warning Signs
With early detection and healing, it has little all basal cell carcinomas (BCC) be safely removed without complications.
Watch for warning signals from BCC such as fresh, changing, or abnormal skin tumors. Doing so ensures early detection when skin cancer is easiest to treat and cure.
- How to Qualify for BCC: 5 Warning Signals
- BCC can be complicated
- What You Can Do
- Rare Skin Cancer
- Skin Cancer Photos
- Skin Cancer Recognition Toolkit
How to Qualify for BCC: 5 Warning Signals
Check for BCC especially on the face, ears, neck, scalp, windows, and back where the skin is most exposed to the sun. But remember, there is a chance it can show up on your body in any location. It is not uncommon for two or more of these warning signals and symptoms to be evident in BCC tumors.
- An open wound that does not heal and has a chance to bleed, pee, or interrupt. Boners have the opportunity to remain present for months. Likewise, they return after healing.
- Reddish or irritated areas on the face, chest, shoulders, arms, legs, skin, any chance of itching, hurting, or causing discomfort.
- Shiny bumps or lumps that are considered mother-of-pearl or peal, pink, reddish, or snow white. The bumps can be brown, black, or brown, even if the person is particularly colored, and can be seen in the normal birthmarks.
- Small iridescent elevations with slightly raised curled edges and a crust in the center. This may develop small vessels over time.
- Flat whitish, yellowish, or waxy colored scar-like areas. The crust is shiny, appears sturdy, and is often not clearly defined. This warning sign can indicate an invasive BCC.
Note: Not all BCCs look the same, so these images are a summary reference to it basal cell carcinoma looks like.
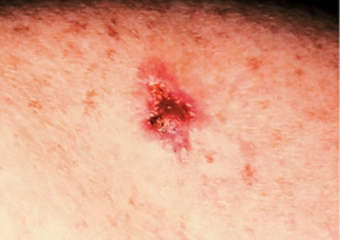
Open non-healing
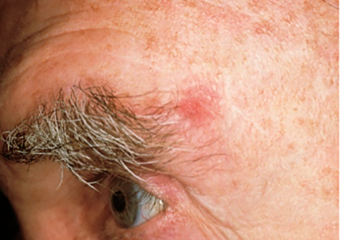
Reddish or irritated areas
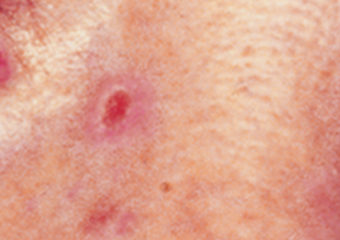
Slightly raised , small iridescent elevations with curled edges and crust in the middle
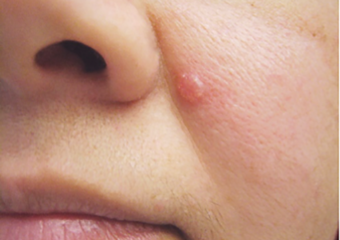
Shiny bumps or lumps
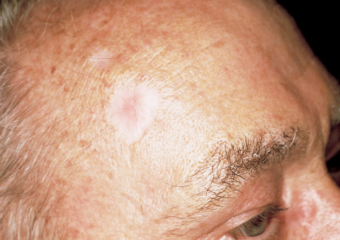
Flat whitish, yellowish, or waxy scar-like areas in color
BCC can be complicated
BCC is not the same as described above. In some people, BCC looks like a noncancerous skin disorder such as psoriasis or eczema. In dark-skinned individuals, more than 50% of BCC is hyperpigmentation (i.e., coffee color).
If in doubt, find it. Follow your own instincts and go to your own dermatologist if you see anything fresh, changeable, or unusual on your skin.
A basal cell carcinoma This way, you can be pigmented in color. Thanks to photo Andrew Alexis, MD, MPH.
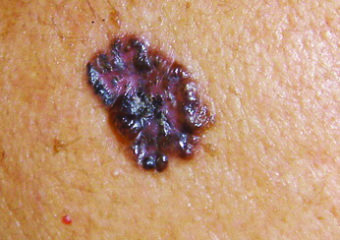
What You Can Do
If you already have BCC, you may develop it, especially in or near the same bright sun.
BCC can come back, even if it is carefully removed for the first time. This is because some cancer cells have the opportunity to remain unaffected after surgery, while others have the opportunity to form roots beyond what is truly visible. BCCs of the nose, ears, and lips are usually more likely to return in the direction of the first two years after surgery.
This is something that can be done to prevent skin damage that could lead to repeated cycles and cancer.
- Be vigilant: pay attention to previously treated areas, pay attention, and consult a dermatologist; if the BCC returns, your doctor may recommend another healing modality, such as MOHS surgery. This is a fairly effective way to prevent and treat recurrence.
- Check yourself on your feet: look for fresh or changing lesions that are growing, bleeding, or not healing. Learn how you can examine your own skin.
- Go to your own dermatologist annually for a professional skin test. They are no substitute for an enthusiast who knows how to detect and treat abnormal skin elevations.
- Follow-up supervision: in case you have already counted BCC or Pavement Cell carcinoma (SCC), or a precursor that looks like actinic keratoconus, it is imperative to consult a physician with the correct statement.
- Sunshine every day: beware of the unprotected effects of ultraviolet radiation. Examine the shade, especially when the sun is considered most intense, and use sunscreen with wide edges, a wide rangy hat, and sunglasses. Radiation Stops. Protecting yourself daily is the most effective way to lower your risk of skin cancer. Add more agreements to prevent skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma of the nose: types, identification, and treatment
Basal cell carcinomas Rose of the nose grows slowly and can be cured if detected early. If you notice unusual spots or bumps on your nose, especially if you spend a lot of time in the fresh air, go to the doctor.
Basal cell carcinoma This is an image of skin cancer. It can develop on parts of the skin exposed to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. This applies to you as well.
When it happens to be your nose that is being noticed, basal cell carcinoma It may look like an elegant yellowish spot, a reddish spot, a fantastic ridge, or an oath you don’t want to heal.
Basal carcinoma It grows slowly and is usually easy to treat. Surgery to remove the tumor is considered the best option. However, radiation, immunotherapy, and cryotherapy may still be used for these options.
This message details the signs, diagnosis, and treatment of skin cancer. of basal cell carcinoma of the nose.
Basal cell carcinoma Here is an image of skin cancer. Within 80% of all skin cancers in humans is basal carcinoma Basal or surface layer. the basal Cellular or surface layer of skin.
Basal cell carcinoma Grows slowly. Typical, basal carcinoma nose can be surgically removed before it spreads to other areas. However, if it remains untreated, the cancer can spread to your bones and surrounding tissue.
Types of basal cell carcinoma
There are different types of basal cell carcinoma These can develop in your nose. These include
- Nodular basal cell carcinoma Nose: Nodules. basal cell carcinomas Forms clear nodules in terms of the skin. It is not uncommon to see blood vessels.
- Sclerosing basal cell carcinoma Nose: Sclerosis. basal cell carcinoma Looks like a small whitish scar that slowly spreads.
- Superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma From the nose: superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma Occurs more frequently on the back than on other skin surfaces. However, it is possible to perform this type of basal cell carcinoma On your nose. It looks like graceful raised skin spots (called “plaques”) that are close to your normal skin color and expand very slowly.
- Pigmented basal cell carcinoma From the nose: coloration basal cell carcinoma It is a nodular or superficial form basal cell carcinoma It occurs in more dark skin tones. This type of basal cell carcinoma can sometimes be confused with melanoma before a biopsy is taken.
Basal carcinoma It appears on the surface of the skin. Basal carcinoma nose is seen on the nose. When basal cell carcinoma first develops, it may be confused with acne, insect bites, age spots, or rashes. Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma To aristoclastic, connect.
- Reddish spots on the nose
- Itching
- Small, rare and shimmering bumps with any chance of blue, brown, or dark spots
- Dull or yellowish flat and hard spots
- Open wounds that do not heal or heal back
- Pink elevation with visible blood vessels with upcoming edges that look like spokes on a wheel
- Irregularities that just bleed
Basal cell carcinoma Can be seen in different ways depending on skin color and shade You can see examples of basal cell carcinoma Image gallery below.
There is no way to predict 100%. basal carcinoma From the nose. However, as with all forms of skin cancer, UV exposure is known to be considered a more significant risk factor. UV radiation can damage the skin and over time can lead to cancer. Additional risk points for basal cell carcinoma Include:
- Reduce. Usage
- Repeat tanning
- Have clear or light skin color
- Exposure to arsenic and certain other chemicals
- Exposure to radiation from previous cancer treatment
- Previous
- Has inflammatory skin conditions
- Has a weakened immune system
- Has human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Smoking
As with most forms of cancer, the risk takes of basal cell carcinoma from nasal cancer with age. People assigned male at birth have a slightly higher risk than those assigned female at birth. However, this is due to the fact that almost all workplaces that people assigned male at birth are solar or radiation related.
Preventing basal carcinoma of the nose
There are steps you can take to protect yourself and your risks basal cell carcinoma Developing a nose. Strategies include
- Limit your own exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Avoid sun exposure.
- Stay in the shade if it is possible.
- Wear sunscreen and apply every 2 hours.
- Wear a hat that is knee-widening.
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection.
- Avoid areas where you can be exposed to harmful chemicals.
- Stop smoking.
- Examine your own skin regularly for the presence of each bump, redness, or abnormal lift.
First Steps in Treatment for basal cell carcinoma In case you notice any unusual skin discoloration or bumps on your nose, your nose should aim for an appointment with your doctor or caregiver.
The physician will ask you about your symptoms. For example, he or she may ask you when you first notice something unusual on your nose. He or she will also ask you what it feels like to be exposed to the sun and whether you have cancer at home.
For the physiological part of the study, they will analyze the areas where they think you have cancer. They have every opportunity to investigate the surrounding areas, including your lymph nodes, which have every opportunity to swell when the cancer has spread.
They will employ a skin biopsy to determine if the area is considered cancerous. In some cases, the entire area is removed during the biopsy. This sometimes dissolves basal cell carcinoma of the nose before the final diagnosis is made.
In other cases, a small sample of the area is taken and sent to a laboratory for study. In both cases, the physician uses small surgical instruments to complete the procedure.
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma The most common treatment is surgery to remove the tumor. The most common treatment is surgery to remove the tumor. During the surgical procedure, the physician removes the cancerous area and a piece of healthy skin around it to ensure that the tumor will not grow further.
A specific type of surgery called MOHS surgery may be performed: during a MOHS operation, the affected skin is removed one layer at a time. Each layer removed is checked for cancer. Layers are removed until all cancerous layers are gone.
If surgery is not possible or treatment is necessary, there are still options
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy has the ability to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. This allows the tumor to heal and stops the spread of the cancer.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy uses freezing temperatures to shrink and destroy small tumors.
- Superficial tumor treatment: Tumors that are fairly close to the skin surface can be treated with these therapies, including nearby chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and immune response modifiers.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a special treatment that helps the immune system find and destroy cancer cells.
The outlook of people with basal cell carcinoma nose are generally flattering.
According to the Cancer Control of South America, within 5, 4 million yanks are diagnosed with some form of cancer each year. of basal cellular or squamous cell carcinoma per year. In addition, each year 2000 yanks are diagnosed with of basal or squamous cell carcinoma. That is 0.004%.
Most deaths basal cell carcinoma nose occurs when people destroy their immune system or when the cancer is treated only when it has spread.
Basal cell carcinomas It develops on the surface of the skin covering the plane of the nose. Base. carcinomas The most common form of skin cancer. However, they are usually still healed.
In most cases, basal cell carcinoma They can be removed from the nose during operation. Occasionally, basal cell carcinoma can also be sent during a skin biopsy test so that the cancer is resolved before a diagnosis is made.
If a non-surgical cure is needed, options include radiation, cryotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Last lick of the doctor on January 4, 2023.






